AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_aao_nanos"
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
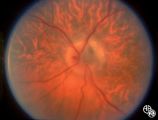 |
Congenitally Tilted Optic Disc | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | Colobomas or defects of the optic nerve may exhibit spontaneous pulsations. Disease/Diagnosis: Coloboma. |
| 27 |
 |
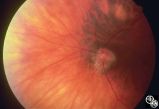
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 28 |
 |
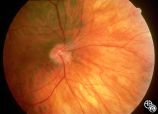
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 29 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 30 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 31 |
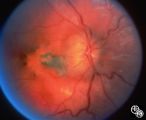 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Joel M. Weinstein, MD | This 8-year-old boy presented with a 2-week history of decreased vision in the right eye. He had undergone a normal MRI and CSF examination, including intracranial pressure, before neuro-ophthalmologic assessment. The fundus photographs and fluorescein angiograms show subretinal neovascularization a... |
| 32 |
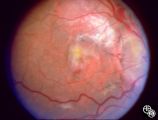 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This patient has known pseudoxanthoma elasticum (an uncommon elastic tissue disorder characterized by plaque-like skin folds [plucked chicken skin] and degeneration of collagen fibers involving multiple systems, including the GI tract and heart), angioid streaks, and optic disc drusen. |
| 33 |
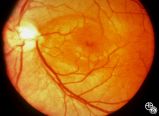 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | An optic pit is a small defect in the optic disc that may be asymptomatic in isolation. Patients may develop an associated serous detachment of the macula. The condition is usually unilateral but may be bilateral. A fluorescein angiogram may demonstrate the serous detachment, and laser photocoagulat... |
| 34 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | Benign tumors of blood vessels (hemangiomas) may occur on the optic nerve and may mimic optic disc edema. Disease/Diagnosis: Optic Nerve Hemangioma. |
| 35 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Rosa A. Tang, MD | This patient has optic disc drusen and evidence of a superimposed optic neuropathy, including loss of visual field, an ipsilateral afferent pupillary defect, and optic atrophy. Although optic disc drusen typically causes visual field loss without visual acuity loss superimposed, ischemic optic neuro... |
| 36 |
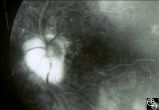 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This 63-year-old man with amblyopia OD was seen for a question of ischemic optic neuropathy with a pale, swollen disc OD. The correct diagnosis is an exophytic capillary angioma of the optic nerve head. Disease/Diagnosis: Capillary Angioma. |
| 37 |
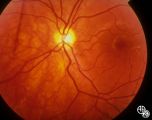 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | Patients with hypoplasia of the optic nerve may have normal or subnormal visual acuity or visual field. The condition may be unilateral or bilateral. Optic nerve hypoplasia is usually idiopathic, but maternal diabetes, or maternal use of anti-epileptic drugs or alcohol are predisposing factors. Opti... |
| 38 |
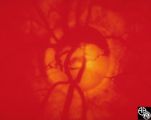 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | Optociliary shunt vessels are venous collaterals that form in response to chronic venous obstruction, shunting the venous blood from the retinal circulation into the choroidal circulation. Although they may be congenital, they may occur in patients with chronic disc edema, following central retinal ... |
| 39 |
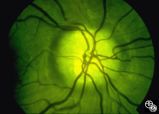 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | This optic disc displays multiple drusen. Note the pseudopapilledema here. One can differentiate this from true papilledema in that there is no obscuration of the vessel by the peripapillary nerve fiber layer as they cross the disc margin. This photograph was taken with barrier filters in place, but... |
| 40 |
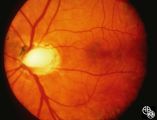 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | An optic pit is a small defect in the optic disc that may be asymptomatic in isolation. The pit can be small or large, and central or peripheral. Disease/Diagnosis: Optic Pit. |
| 41 |
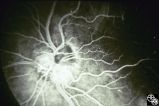 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Larry P. Frohman, MD | This 63-year-old man with amblyopia OD was seen for a question of ischemic optic neuropathy with a pale, swollen disc OD. The correct diagnosis is an exophytic capillary angioma of the optic nerve head. Disease/Diagnosis: Capillary Angioma. |
| 42 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 43 |
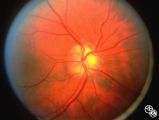 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This image shows drusen that are especially prominent superotemporally. Pair with 92_64 and 92_67. |
| 44 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Joel M. Weinstein, MD | This 8-year-old boy presented with a 2-week history of decreased vision in the right eye. He had undergone a normal MRI and CSF examination, including intracranial pressure, before neuro-ophthalmologic assessment. The fundus photographs and fluorescein angiograms show subretinal neovascularization a... |
| 45 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | William Fletcher Hoyt, MD | This patient demonstrates bilateral tilted optic discs. Patients with this congenital optic disc anomaly may be asymptomatic or have bitemporal visual field defects that do not respect the vertical midline. Disease/Diagnosis: Tilted Discs. |
| 46 |
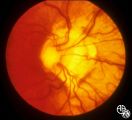 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Thomas R. Wolf, MD | Patients with midline closure defects may exhibit abnormalities in the optic nerve, choroid, retinal pigment epithelium or retina. Anterior closure defects may result in colobomas of the structures of the anterior segment, such as the iris. Disease/Diagnosis: Coloboma. |
| 47 |
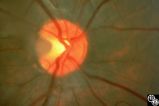 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | A 10-year-old girl had central visual loss due to this optic pit. Disease/Diagnosis: Optic Pit. |
| 48 |
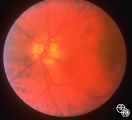 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This is a photograph of peripheral drusen. The paired image 92_69 demonstrates the typical autofluorescence. |
| 49 |
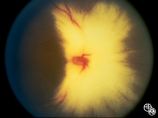 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Normally, there is no visible myelination of the nerve fiber layer in the retina. Occasionally, visible myelination occurs that takes on a characteristic white, arcuate, feathery appearance that follows the contour of the nerve fiber layer. Disease/Diagnosis: Myelinated Nerve Fiber. |
| 50 |
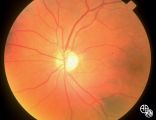 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Roger Turbin, MD | Shown are the fundi of a - year old child with dominant optic atrophy, 20/200 OU. Pair with 1996_59. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital optic atrophy. |
