The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
 |
Ventricular asystole - marquette | Ventricular asystole - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 227 |
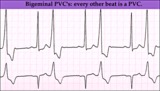 |
Ventricular bigeminy - marquette | Ventricular bigeminy - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 228 |
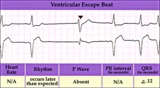 |
Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Ventricular escape beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 229 |
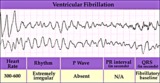 |
Ventricular fibrillation - marquette | Ventricular fibrillation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 230 |
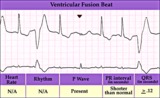 |
Ventricular fusion beat - marquette | Ventricular fusion beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 231 |
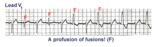 |
Ventricular fusion beats | Fusion beats occur when two or more activation fronts contribute to the electrical event. These may occur in the atria or in the ventricles. In this example the ventricular fusions are the result of simultaneous activation of the ventricles from two foci, the sinus node and a ventricular ectopic... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 232 |
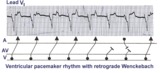 |
Ventricular paced rhythm with retrograde wenckebach | Retrograde atrial captures from a ventricular paced rhythm are occurring with increasing R-P intervals; i.e., retrograde Wenckebach. The ladder diagram indicates that after the blocked retrograde event, a single sinus P wave is seen dissociated from the ventricular rhythm. | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 233 |
 |
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm | Note the small pacemaker spikes before the QRS complexes in many of the leads. In addition, the QRS complex in V1 exhibits ventricular ectopic morphology; i.e., there is a slur or notch at the beginning of the S wave, and>60ms delay from onset to QRS to nadir of S wave. This rules against a suprav... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 234 |
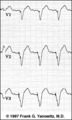 |
Ventricular Pacemaker Rhythm: V1-3 | Note the small pacemaker spikes before the QRS complexes. In addition, the QRS complex in V1-3 exhibits ventricular ectopic morphology; i.e., there is a slur or notch at the beginning of the S wave, and >60ms delay from onset to QRS to nadir of S wave. This rules against a supraventricular rhythm wi... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 235 |
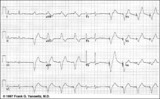 |
Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Ventricular pacemaker: demand mode functioning | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 236 |
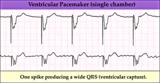 |
Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Ventricular pacing in atrial fibrillation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 237 |
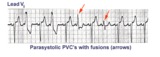 |
Ventricular parasystole | In ventricular parasystole, non-fixed coupled PVC's occur at a common inter-ectopic interval. Fusion beats, indicated by arrows, are often seen. Fusions occur when the sinus impulse entering the ventricles find the ventricles already partially depolarized by the parasystolic focus. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 238 |
 |
Ventricular tachycardia - marquette | Ventricular tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 239 |
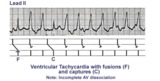 |
Ventricular tachycardia with AV dissociation, captures, and fusions | Approximately 50 percent of ventricular tachycardias are associated with AV dissociation. In these cases atrial impulses can enter the ventricles and either fuse with a ventricular ectopic beat or completely capture the ventricles. This ladder diagram illustrates these events. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 240 |
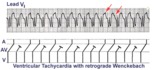 |
Ventricular tachycardia with retrograde wenckebach | Approximately 50 percent of ventricular tachycardias are associated with AV dissociation. The other 50 percent have retrograde atrial capture. This example shows ventricular tachycardia with retrograde Wenckebach. The retrograde P waves are hard to find, but the arrows are of some help. | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 241 |
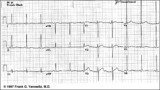 |
Voltage criteria for LVH | Voltage criteria for LVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 242 |
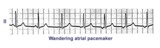 |
Wandering atrial pacemaker | Wandering atrial pacemaker is a benign rhythm change where the pacemaker site shifts from the sinus node into the atrial tissues. P-wave morphology varies with the pacemaker site. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 243 |
 |
Wandering baseline artifact - marquette | Wandering baseline artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 244 |
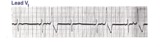 |
What are those funny looking beats???? | The differential diagnosis of funny-looking-beats, or FLB's, primarily considers beats of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction and ventricular ectopic beats. In this example the two FLB's have an easily seen ectopic P wave before them; therefore these are PAC's with RBBB aberration. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 245 |
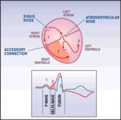 |
WPW diagram | The short PR interval is due to a bypass track, also known as the Kent pathway. By bypassing the AV node the PR shortens. The delta wave represents early activation of the ventricles from the bypass tract. The fusion QRS is the result of two activation sequences, one from the bypass tract and one... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 246 |
 |
WPW Type Pre-excitation: Precordial Leads | WPW Type Pre-excitation: Precordial Leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 247 |
 |
WPW type preexcitation | Note the short PR and the subtle delta wave at the beginning of the QRS complexes. The delta wave represents early activation of the ventricles in the region where the AV bypass tract inserts. The rest of the QRS is derived from the normal activation sequence using the bundle branches. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 248 |
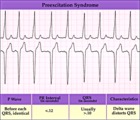 |
WPW type preexcitation - marquette | WPW type preexcitation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
