The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
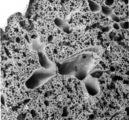 |
Survey of lung parenchym (gerbil) | Scanning electron microscopy. The photograph shows (1) bifurcation of several bronchi in the lung parenchym with alveoli (2). The long arrows indicate the route of alveolar ducts (4 ↕ length, and cross 4↑). Pulmonary vessels (3). | Lung parenchym; Pulmonary vessels | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 227 |
 |
Surface of trachea epithelium (rat) | Scanning electronmicroscopy. There is an abundancy of cilia with interspersed protrusions (↓) of goblet cells due to apical secretion. | Pseudostratified epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 228 |
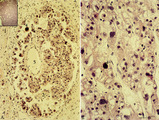 |
Choriocarcinoma (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin-eosin. (A) Inset: Survey tumor. Within the uterus (1) a choriocarcinoma forms solitary or multiple nodules composed of hemorrhagic necrotic areas (2) surrounded by neoplastic cells. It resembles an early implanted blastocyst with aggregations of mononuclear lighter-stained cyt... | choriocarcinoma; placenta; uterus; cytotrophoblast; GTD (gestational trophoblastic disease) | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 229 |
 |
Epithelial lining of terminal bronchiolus (golden hamster) | Electron microscopy (low magnification). Two major epithelial cell types line the bronchiolus: (1) the ciliated cells with many organelles, and (2) the non-ciliated cells or Clara cells well provided with organelles, especially agranular endoplasmic reticulum and depending on their activity, numerou... | Terminal bronchiolus; Ciliated epithelium ; Clara cells; Neuro-endocrine cells; Pneumocytes; Alveolar cell types; Interstitium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 230 |
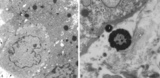 |
Electron microscopy of tertiary villus (human placenta, midpregnancy) | In the left photograph (A) is shown part of a tertiary villus with the organelle-rich cytoplasm of a syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 1). Below a single electron-light linked cytotrophoblast cell (CTC or Langhans cell, 2) covered by the STC. A higher magnification of another CTC (right photograph) sh... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast; electron microscopy; placental barrier | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 231 |
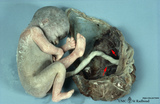 |
Normal term placenta with umbilical cord attached to the fetus (human) | The macroscopy shows the expelled placenta as a discoidal mass with a circular outline about 15-20 cm in the ruptured amnionitic and chorionic sacs. Amnion and smooth chorion (chorion leave) are fused and continuous with the margins of the placenta. The fetal surface (inner surface) is covered by... | placenta; amnion; chorion; umbilical cord; fetus | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 232 |
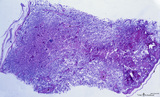 |
Survey of the intervillous space with villi (human placenta, full-term) | Stain: Perjodic Acid Schiff reaction (PAS). At the right and left side the chorionic plate (1) with few cross-sectioned umbilical vessels (2), at (3) a detached amnion. Cross-sections of thick stem villi (4) at the fetal side ramify into terminal villi (tertiary) that are found stuffed (due to fix... | placenta; stem villus; syncytiotrophoblast; amnion | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 233 |
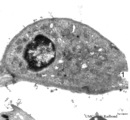 |
Brush cell in lung (rat) | Electron microscopy. In the proximal as well as in the terminal airways a special type of cell can be observed, the so-called brush (-border) cell. In this picture this cell is located in the alveolar space. At (1) the brush border of thick plump microvilli. In the cytoplasm a Gogi area, mitochondri... | Brush cell | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 234 |
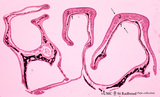 |
Survey of the nasal conchae (dog, isolated turbinate bones) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. The conchae (turbinates) consist of three parts: the inferior, middle and superior turbinate bones (3, black-stained); they are covered by a respiratory mucosa (1) or by an olfactory mucosa (2). In humans only a small part of the superior concha exhibits olfactory epith... | Conchae nasales; Olfactory epithelium; Respiratory epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 235 |
 |
Transitional zone in the middle part of nasal vestibulum (comparable with red zone or vermilion border of lip, human) | Stain: Azan. At the right slightly cornified squamous epithelium (1) with small dermal papillae (2) and numerous blood vessels (3). To the left the transition to pseudostratified epithelium (4). In the submucosa branching seromucous nasal glands with draining ducts (5). | Stratified epithelium; Pseudostratified epithelium; Nasal glands; Seromucous glands | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 236 |
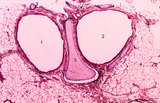 |
Survey of bronchus and lung parenchym (human, adult) | Stain: Azan. Lumina of bifurcated bronchi (1, 2). Thin plates of hyaline cartilage (3) and connective tissue surround the bronchi. Arrows (→) indicate lung alveoli with black-stained patches of carbon deposits. (4) Lung parenchyma with alveoli. | Lung parenchym | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 237 |
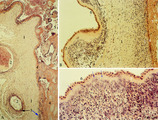 |
Chorioamnionitis (human) | Histologically chorioamnionitis describes the progression of the inflammatory process. Bacteria firstly colonized the chorioamniotic surface. In first two days polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMN) migrate to the chorion (chorionitis) marginate and adhere to the bottom of the chorionic plate (stage 1... | chorioamnionitis; placenta; trophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 238 |
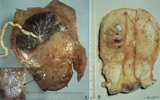 |
Partial hydatidiform mole and invasive mole (human) | (A) Macroscopy: The partial mole (1) occupies a large part of the placenta and is distinct from the normal chorionic plate where the umbilical cord (2) inserts eccentrically with branches of the umbilical vessels. The inset shows a circumscript area with swollen transparent grape-like vesicles (chor... | partial hydatidiform mole ; chorioadenoma | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 239 |
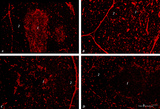 |
Immunohistochemistry of thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) Medulla. (2) Cortex. (A): Staining with a monoclonal antibody against vimentin illustrates that vimentin is localised in the stromal cells of the connective tissue of the capsule, of the septa or trabeculae that invade the cortex (2) and overwhelmingly ... | vimentin; laminin; fibronectin; ED2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 240 |
 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left and right: survey of lymph nodes, compare the individual differences between the nodes. The pictures display the cortex (1) with capsule (3), and the medulla (2). The cortex consists of (secondary) follicles displaying a clear germinal centre (4). The paracortex (T cell area) is ... | follicle; paracortex; cortex; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 241 |
 |
Normal term placenta (human) | (A) Left (fetal surface): 30-90 cm long umbilical cord (1), remnant of ruptured transparent amnion (2→) , near the eccentric attachment of the umbilical cord to the chorion plate ramification of the umbilical vessels (3) (arteries are smaller than the veins). (B) Right (maternal surface). The su... | placenta; amnion; chorion plate; cotyledon | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 242 |
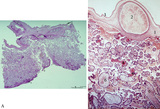 |
Survey and detail of the chorionic plate and intervillous space (human placenta, full-term) | Stain: (A) Perjodic acid-Schiff reaction (PAS); (B) Hematoxylin-azophloxine. (A) At the top the chorionic plate (1) with cross-sections of umbilical vessels (2). At (3) the folded amnion covering the chorionic plate. Ramifications of thicker stem villi (6) demonstrate free-floating terminal villi ... | placenta; chorionic plate; amnion; terminal villi | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 243 |
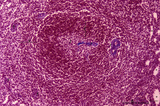 |
Spleen with central artery in secondary lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Azan. The white pulp consists of (1) a cross-section of the central artery, (2) the germinal centre with few branches of the central artery; the mantle zone (3) and the marginal zone (4) surrounded by a perilymphoid zone around the nodule. The perilymphoid zone is composed of concentricall... | germinal center; PALS; central artery; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 244 |
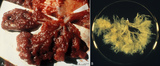 |
Fetal cotyledons (normal term human placenta) | After dissection of one placental lobe several cotyledons (2) are visible in (A). Each fetal cotyledon (2) consists of a main stem villus (1) and all its branches. (B) After trypsinization of a cotyledon the tree of arborisation of the stem villus and its branches becomes visible. (By courtesy... | placenta; cotyledon; villus; trypsinization | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 245 |
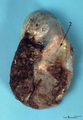 |
Macroscopy of fetus (human) | The fetus (1)is completely wrapped in a shiny transparent amnion (2) and closely associated with the brown-coloured placenta (3). (By courtesy of the Museum of Anatomy and Pathology, University Medical Center, St. Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands) | fetus; placenta; amnion | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 246 |
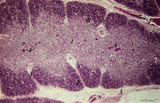 |
Thymus (human, newborn) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The thymus is a bilobed lymphoepithelial organ derived as an outgrowth from the third branchial (pharyngeal) pouch, and situated in the anterior mediastinum. Each lobe is divided into multiple lobules by fibrous septa or trabeculae (3). Each lobule consists of an outer co... | epithelioreticular cells (ERC); thymus hormones; Hassalls corpuscle ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 247 |
 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on CD3-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section.. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the dark-blue stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thy... | cyclophosphamide; CD3 monoclonal antibody; lymphoid tissue ; immunosuppression | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 248 |
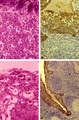 |
Follow-up of the process of diapedesis through stratified epithelium of the palatine tonsil (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (human) | Stain: (A, C) Azan and (B, D) anti-keratin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB) on frozen section, counterstained with hematoxylin. (1) (keratinized) stratified squamous epithelial cells. (2) between desquamated epithelial cells the spaces are filled with infiltrated l... | stratified squamous epithelial cells; GALT | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 249 |
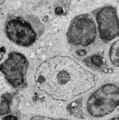 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Within the thymic cortex a type II epithelioreticular cell or so-called (sometimes multinucleated) thymic nurse cell (TNC) shows a characteristic electron-light nucleus and nucleolus (1). The branches are squeezed between the thymocytes (2). In the cytoplasm a variety of empty a... | MHC class I and II expression; epithelioreticular cell type I and II; thymic nurse cell TNC; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 250 |
 |
Corpuscles in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A: Several thymic (Hassall's) corpuscles (*) of varying sizes within the medulla (1). The Hassall bodies are surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules. The outer shell consists of more layers of close packed concentrically arranged cells with light-... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
