The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
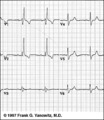 |
RBBB: Precordial leads | RBBB: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 227 |
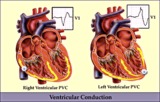 |
RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 228 |
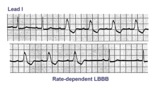 |
Rate-dependent LBBB | In this rhythm strip of sinus arrhythmia, the faster rates have a LBBB morphology. In some patients with a diseased left bundle branch, the onset of LBBB usually occurs initially as a rate-dependent block; i.e., the left bundle fails to conduct at the faster rate because of prolonged refractoriness... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 229 |
 |
Reduction of 2-enoyl acyl carrier peptide | A 2-enoyl acyl group on the acyl carrier peptide is reduced by NADPH in a reaction catalyzed by enoyl acyl carrier peptide reductase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 230 |
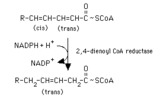 |
Reduction of a 2,4-dienoyl CoA | The reduction of 2,4-dienoyl CoA by NADPH is a step in the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. It is ironic that a reduction reaction is a required step in a process that is oxidative. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 231 |
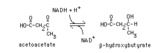 |
Reduction of acetoacetate | Acetoacetate is reduced by NADH in a reversible reaction catalyzed by beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. This reaction is the source of beta-hydroxybutyrate in the blood of individuals with ketosis. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 232 |
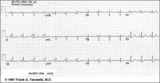 |
Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) & Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) | RAE is recognized by the tall (>2.5mm) P waves in leads II, III, aVF. RVH is likely because of right axis deviation (+100 degrees) and the Qr (or rSR') complexes in V1-2. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 233 |
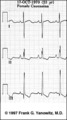 |
Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 234 |
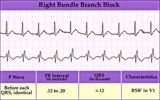 |
Right Bundle Branch Block | Right Bundle Branch Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 235 |
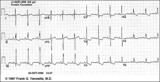 |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) & Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) | In this case of severe pulmonary hypertension, RVH is recognized by the prominent anterior forces (tall R waves in V1-2), right axis deviation (+110 degrees), and P pulmonale (i.e., right atrial enlargement). RAE is best seen in the frontal plane leads; the P waves in lead II are >2.5mm in amplitud... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 236 |
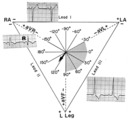 |
Right axis deviation: QRS axis = +130 degrees | Lead aVR is almost isoelectric; lead I is mostly negative, and lead III is very positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +130 degrees. Note that the slightly more positive AVR moves the axis slightly beyond +120 degrees; i.e., closer to the + pole of the aVR lead. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 237 |
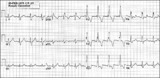 |
Right bundle branch block (RBBB) | Right bundle branch block (RBBB) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 238 |
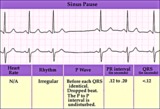 |
SA exit block - marquette | SA exit block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 239 |
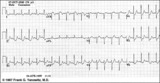 |
ST segment depression | ST segment depression is a nonspecific abnormality that must be evaluated in the clinical context in which it occurs. In a patient with angina pectoris ST depression usually means subendocardial ischemia and, unlike ST elevation, is not localizing to a particular coronary artery lesion. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 240 |
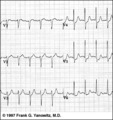 |
ST segment depression: precordial leads | ST segment depression: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 241 |
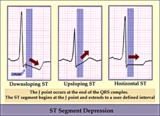 |
ST segment diagram - marquette | ST segment diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 242 |
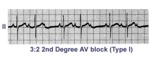 |
Second degree AV block, type I, with 3:2 conduction ratio | There are two types of 2nd degree AV Block. In this example of Type I or Wenckebach AV block there are 3 P waves for every 2 QRSs; the PR interval increases until a P wave fails to conduct. This is an example of group beating. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 243 |
 |
Second degree AV block, type I, with bradycardia-dependent RBBB | An interesting and unusual form of rate-dependent bundle branch block. Normal sinus rhythm at 85 bpm is present with a 3:2 and 2:1 2nd degree AV block. The progressive PR prolongation in the 3:2 block makes this a type-I or Wenckebach block.Long cycles end in RBBB; short cycles have normal QRS dur... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
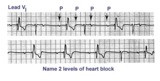
| 244 |
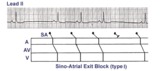 |
Sino-atrial exit block, type I or wenckebach | This example illustrates 2nd degree sino-atrial exit block. In type 1 S-A block the conduction time between sinus firing and atrial capture progressively prolong, but this cannot be seen on the ECG tracing; type I exit block is inferred if the P-P intervals gradually shorten before the pause and if... | Wenckebach AV Block; Ladder Diagram | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 245 |
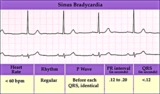 |
Sinus bradycardia | Sinus bradycardia | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 246 |
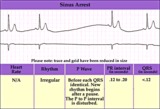 |
Sinus pause or arrest - marquette | Sinus pause or arrest - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 247 |
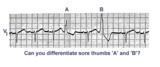 |
Sore thumbs | Two funny looking premature beats are seen in this rhythm strip. Beat A is preceded by a PAC which distorts the T wave, making this an aberrantly conducted PAC. Beat B is a PVC. The notch on the down slope of the QRS complex clearly identifies this as a PVC and not aberrancy. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 248 |
 |
Stearic acid structure | Stearic acid is a typical long chain saturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 249 |
 |
Stearic, oleic and linoleic acid structures | Stearic, oleic and linoleic acid structures | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 250 |
 |
Structures of the ketone bodies | These are the structures of the ketone bodies. Acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are important physiological substrates. Acetone is a byproduct, and is not metabolized further. It is excreted in the urine and in expired air. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
