The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
 |
Glands of GI Tract | Higher magnification image of liver stained with PAS showing different levels of glycogen storage in hepatocytes. Some hepatocytes have numerous glycogen granules, whereas there are other hepatocytes without glycogen granules, indicating depletion of stored glycogen. UCLA Histology Collection. | glycogen; Liver; PAS stain; gastrointestinal tract | UCLA Histology |
| 227 |
 |
Ovary | This image shows a small region of a corpus luteum within the stroma. The somewhat folded layer of granulosa lutein cells is quite evident. Even at this magnification, the smaller theca lutein cells are identifiable. A vascular space can also be recognized in this image. UCLA Histology Collection. | corpus luteum; Ovary | UCLA Histology |
| 228 |
 |
Thymus - Young Thymus | Young thymus, showing cortex and portions of the medulla. Note a Hassals corpuscle in the medulla. ( This is a diagnostic feature of the thymus.) UCLA Histology Collection. | cortex; lymphoid organ | UCLA Histology |
| 229 |
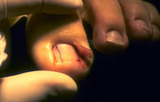 |
Ingrown nail | This shows the nail plate just barely attached. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 230 |
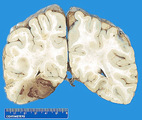 |
Recent hemorrhagic infarction 2 | Recent hemorrhagic infarction 2 | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 231 |
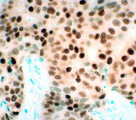 |
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 232 |
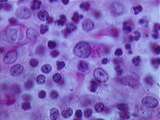 |
Thymus - Epithelial Reticular Cells | This image from the medulla shows many epithelial reticular cells, which have a pale cytoplasm, large nucleus, and prominent nucleolus. These cells form a meshwork which contains developing lymphocytes. One macrophage or PAS cell is visible. PAS stains its phagocytic inclusions bright pink. Note the... | epithelial reticular; Hassall's corpuscle; PAS | UCLA Histology |
| 233 |
 |
Skin | This high power view illustrates the relationship of epidermal pegs, which invaginate into the dermis, with the dermal papillae which extend into the epidermis. This sample has a highly pigmented basal layer, composed of keratinocytes with melanosomes. Melanocytes produce the pigment melanin and are... | epidermis; Skin | UCLA Histology |
| 234 |
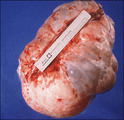 |
Mucinous cystadenoma | These tumors comprise 20% of all neoplasms, and 50% of ovarian neoplasms found in women less than 20 years of age. They are frequently multiloculated. The favored hypothesis for their origin is metaplastic surface epithelium as they have a predominance of endocervical gland type epithelium. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 235 |
 |
Ovarian tumor | A large vertical incision allows delivery and excision of an ovarian neoplasm. Pelvic washings for cytology and a frozen section rule out a malignancy. The cyst is excised carefully to avoid spilling contents into the abdomen. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 236 |
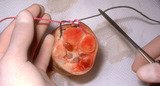 |
Excision: suturing | The double loop is tightened by pulling the hands into their natural position, but the knot cannot be adequately tightened by pulling in that direction; the knot must be tightened by pulling the suture ends along the length (long axis) of the wound. (This is shown in the following slide) | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 237 |
 |
Pituitary | Because of its physiological importance, several images of the pars distalis are included. In this one, recognize bluish basophils, abundant reddish acidophils, a probable chromophobe (with no cytoplasmic granules), and red blood cells. UCLA Histology Collection. | pars distalis; Pituitary | UCLA Histology |
| 238 |
 |
Scalpel | This is a cross-sectional view demonstrating the blade angled away from the center of the ellipse. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 239 |
 |
Adrenal gland neoplasm | Adrenal gland neoplasm | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 240 |
 |
Medullary carcinoma | Medullary carcinoma | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 241 |
 |
Skeletal Muscle | Note the alternating cross sectional and longitudinal fascicles of skeletal muscle that are characteristic of the tongue. Also note the difference in appearance of the connective tissue space. Identify the pockets of adipose tissue within this section, as well as the prominent nerve bundles, and blo... | Skeletal Muscle; Tongue | UCLA Histology |
| 242 |
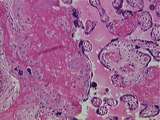 |
Placenta | This image is very useful for differentiating the fetal and maternal components of the placenta . One can readily identify the maternal blood space , fetal villi including one obvious tertiary villus . Fibrinoid is present in the area of fetal villi as well as in a region dominated by maternal decid... | Placenta | UCLA Histology |
| 243 |
 |
Connective Tissue | This low power view of the monkey heel shows epidermis, dermal connective tissue, a sweat gland, and the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the dark-pink heel bone. Fatty tissue can be seen in the bone marrow cavity. UCLA Histology Collection. | Connective Tissue; epidermis; tendon | UCLA Histology |
| 244 |
 |
Peripheral Nervous System | Very low power view of two myelinated nerves. Good for epineurium and perineurium. Osmium stained so myelin is stained. UCLA Histology Collection. | Peripheral Nervous System | UCLA Histology |
| 245 |
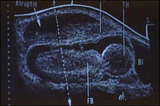 |
Ultrasound of placental abruption | The fetal body and bladder are labeled FB, and BL, respectively. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 246 |
 |
Dermatitis | Best control of the dermatitis is achieved by first soaking the skin for 10 minutes in lukewarm water. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 247 |
 |
Thymus - Medulla | In this image of the medulla, identify lymphocytes, PAS cells, and an epithelial reticular cell. UCLA Histology Collection. | medulla; PAS | UCLA Histology |
| 248 |
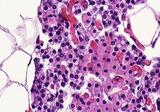 |
Normal parathyroid | Normal parathyroid | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 249 |
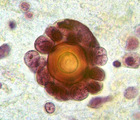 |
Psammoma body | Psammoma body | Knowledge Weavers Pathology | |
| 250 |
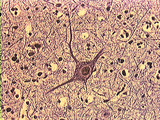 |
Central Nervous System | Pyramidal cells of the cortex have several dendrites and one axon emanating for the cell body. The cell body has a nucleus with a nucleolus. The dendrites are branched and taper as they leave the cell body. One slender axon can be seen emerging from the cell body. Darkly stained nuclei of neuroglial... | Brain; Central Nervous System; cortex; pyramidal cell | UCLA Histology |
