A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
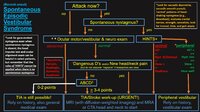 |
An Approach to the Patient with (Recent Onset) Spontaneous Episodic Vestibular Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the recent onset of the spontaneous (unprovoked) episodic vestibular syndrome (EVS), especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors ... | Image |
| 2 |
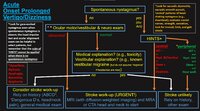 |
An Approach to the Patient with Acute Onset Prolonged Vertigo | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the acute onset prolonged vertigo, especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors are present. However, young patients can suffer fr... | Image |
| 3 |
 |
Ocular Motor & Vestibular Features of the MLF Syndrome (Figures 1, 2, and 3) | This 61-year-old woman with HTN and DM presented for evaluation of acute onset diagonal diplopia. Adduction OS was about 60% of normal while medialization OS improved with convergence. In right gaze, dissociated abducting nystagmus was present OD, and there was a clear adduction lag when asking he... | Image |
| 4 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Features and Pseudo-MG Lid Signs in Miller Fisher Syndrome (Figure 1) | This is a 51-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, acute onset dizziness and diplopia that developed over three days following two weeks of upper respiratory infection and bacterial conjunctivitis. When she was initially seen as an outpatient, nystagmus was noted to the right and left, and a ... | Image |
| 5 |
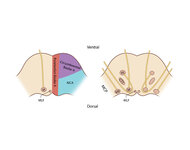 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons | In this axial section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th (VII) and 8th (VIII) fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery, AICA territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied b... | Image |
| 6 |
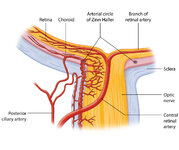 |
Figure 27: Vascular Supply of the Optic Nerve Head, Choroid and Retina | The ophthalmic artery is a branch of the internal carotid artery, which in turn, supplies the posterior ciliary (to choroid and outer retina) and central retinal (to inner retina) arteries. The central retinal artery (CRA) enters the optic nerve about 1 cm posterior to the globe, and an embolus may ... | Image |
| 7 |
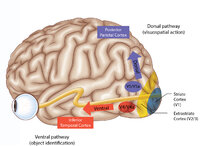 |
Figure 43: How the Brain Makes Sense of What It Sees - The Dorsal and Ventral Visual Pathways, and a 3 Tiered Approach to Vision | 1) Ventral ("what") stream - this begins with the ‘P' retinal ganglion cells à parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN, 3-6) à V1/striate cortex (in blue) à V4/V4a (fusiform and lingual gyri) à occipitotemporal regions. 2) Dorsal ("where") stream - this begins with the ‘M... | Image |
| 8 |
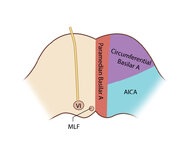 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons (Supplement) | Image | |
| 9 |
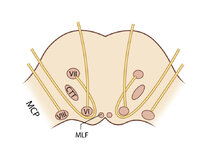 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons (Supplement) | Image | |
| 10 |
 |
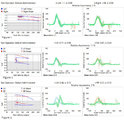
CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) Figure | CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) is a genetic condition consisting of slowly progressive late-onset ataxia, bilateral vestibulopathy, sensory neuropathy, chronic cough, and autonomic dysfunction. While the term vestibular areflexia typically implies bilateral... | Image |
| 11 |
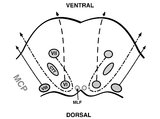 |
Pons: 6th, 7th, 8th, and Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomy | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th and 8th fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied by a + ipsilateral... | Image |
| 12 |
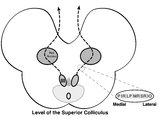 |
Central Anatomy of the Third Nerve | Seen here is an axial section of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus. The paired nuclei are located ventral to the periaqueductal grey, and the midline central caudal nucleus (CCN) is located between the right and left nuclei. The CCN sends projections to bilateral levator palpebrae... | Image |
| 13 |
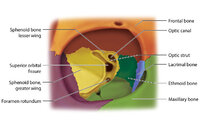 |
Figure 17: Bony Structures Relevant to the Orbit | The frontal, sphenoid, maxillary, ethmoid, and lacrimal bones make up the orbit. Structures passing through the optic canal include the optic nerve, oculosympathetic tract and ophthalmic artery. Structures passing through the superior orbital fissure include the superior ophthalmic vein, cranial ner... | Image |
| 14 |
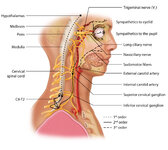 |
Figure 1: Oculosympathetic Pathway for Pupillary Dilation | The oculosympathetic tract is an uncrossed pathway that begins in the hypothalamus, with fibers descending in the brainstem (1st order, commonly affected in a lateral medullary syndrome), synapsing in the lower cervical/upper thoracic spinal cord (interomediolateral cell columns of C8-T2, also refer... | Image |
| 15 |
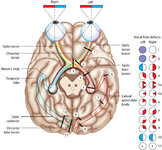 |
Figure 24: Typical Visual Field Defects Associated with Discrete Lesions Along the Visual Pathways | Specific monocular or binocular visual field defects can be highly localizing when the neuroanatomy of the visual pathways is understood. The temporal visual field corresponds to the nasal retina, while the nasal visual field corresponds to the temporal retina. 1) Left optic nerve lesion - while an ... | Image |
| 16 |
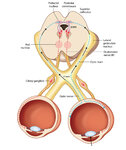 |
Figure 2: Parasympathetic Pathway for Pupillary Constriction | A bright light is shone in one eye, light enters the pupil and hyperpolarizes retinal photoreceptors which activates retinal ganglion cells. These signals propagate along the optic nerves, chiasm, optic tracts, and fibers responsible for the light reflex then synapse in the dorsal midbrain (prior to... | Image |
| 17 |
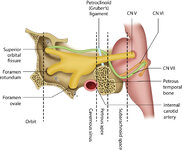 |
Figure 46: The Course of the 6th (VI) Nerve | The sixth nucleus is located dorsally, adjacent to the 4th ventricle, in the lower pons. The genu of the facial (7th) nerve wraps around the 6th nucleus, creating the facial colliculus, which bulges into the 4th ventricle. After the 6th nerve leaves the pons, it follows a vertical course along the c... | Image |
| 18 |
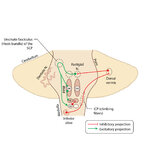 |
Figure 50: Anatomy and Physiology of the Saccadic Pathways | When a saccade is desired (or reflexively triggered), signals project from the saccade-related cortical eye fields to the superior colliculus, which serves to integrate and relay commands to the saccade generating brainstem circuitry. The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to... | Image |
| 19 |
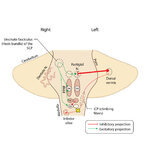 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria | A lesion of the left lateral medulla and inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) will cause decreased climbing fiber inhibition of the left dorsal vermis causing simple-spike (inhibitory) discharge of Purkinje cells to increase. Increased Purkinje cell firing leads to increased inhibition of the ipsilate... | Image |
| 20 |
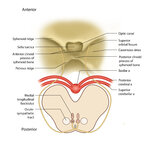 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria (Supplement) | Image | |
| 21 |
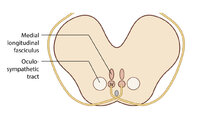 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria (Supplement) | Image | |
| 22 |
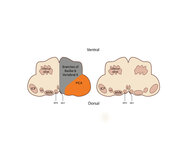 |
Figure 53: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy Relevant to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | This axial section of the medulla highlights those structures that, when damaged, are responsible for the vestibular and ocular motor features of the Wallenberg syndrome. The nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH) and medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) complex is important for horizontal gaze-holding (neu... | Image |
| 23 |
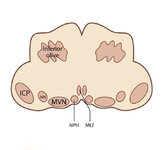 |
Figure 53: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy Relevant to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome (Supplement) | Image | |
| 24 |
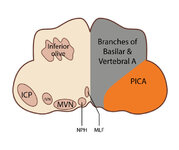 |
Figure 53: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy Relevant to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome (Supplement) | Image | |
| 25 |
 |
Figure 64: The Course of the 3rd (III) Nerve | The 3rd nucleus lies at the ventral border of the periaqueductal gray matter, at the level of the superior colliculus. In between the two nuclei is the midline central caudal nucleus (CCN), which innervates bilateral levator palpebrae muscles (explaining how a unilateral nuclear 3rd can cause bilate... | Image |
