Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL230
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
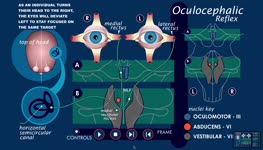 |
Oculocephalic Reflex Animation | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD; Quentin Roper | Animation describing the vestibuloocular reflex. | Vestibuloocular Reflex; Vestibular Ocular System |
| 2 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration Third Nerve | Gregory P. Van Stavern, MD | 48 year old woman S/P rupture and repair of right sided posterior communicating artery aneurysm Video shows residual partial right third nerve palsy, with aberrant regeneration, causing a pseudo Von Graefe's sign (elevation of the right upper eyelid with attempted infraduction of the right eye) | Aberrant Regeneration Third Nerve; Third Nerve Palsy |
| 3 |
 |
Superonasal Transconjunctival Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (stONSD) | Kevin E. Lai, MD; Kenneth C. Lao, MD; Peter L. Hildebrand, MD; Bradley K. Farris, MD | This video demonstrates the surgical technique and outcomes of a modified medial transconjunctival approach to optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD). Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema; Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH). | Superonasal Transconjunctival Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD); Surgical Technique |
| 4 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch Sign | Raed Behbehani, MD | Cogan's lid twitch sign is a twitch sign of he upper lid upon looking straight from a sustained downgaze position. It is associated with Ocular Myasthenia Gavis. | Myasthenia; Ptosis; Lid Twitch |
| 5 |
 |
Congenital Oculomotor Apraxia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Congenital Ocular Motor Apraxia is an uncommon condition that causes children to have difficulty moving their eyes horizontally or from side to side. They are usually unable to quickly move their eyes from side to side and often have to turn their head (head jerking) and not just their eyes to track... | Oculomotor Apraxia |
| 6 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | PAN is a nystagamus characterized by a cycle of uniderectional jerk nystagamus for 60-90 sec , a pause for 10-20 sec and a a cycle of a jerk nystagmus in the opposite direction for 60-90 sec. It is found in brain stem and cerebellar conditions as well as ocular albinism ( as in this patient). | Periodic Alternating Nystagmus |
| 7 |
 |
Ocular Neuromyotonia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Ocular Neuromytonia is a characterised by by paroxysmal tonic contraction of the extraocular muscles supplied by the oculomotor nerve. It is has been reported after cranial radiation therapy, especially to the sellar-parasellar region and from compressive lesions such tumours or aneurysms. The patho... | Ocular Neuromyotania |
| 8 |
 |
Upbeat Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD, | A patient with a brain stem syndrome due to demyelination and upbeat nystagmus. | Upbeat Nystagmus |
| 9 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | This nystagmus localizes to lesions supra/parasellar region (Large sellar and hypothalamic lesion) and is characterized by a see saw movement of elevation/intorsion of one eye and depression/extorsion of the other eye in a pendular fashion. This patient had a large pituitary macro-adenoma with supra... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
| 10 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | See-saw nystagmus is a localizing nystagmus to lesions of the sellar and parasellar region. "It's characterized by synchronous elevation and intorsion of one eye and depression and extorsion of the contra lateral eye . This patent has a craniopharyngioma, which was operated twice, optic atrophy and ... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
| 11 |
 |
Parinaud Syndrome | Raed Behbehani, MD | Parinaud syndrome, as called dorsal midbrain syndrome, is due to dorsal midbrain lesions from compression (e.g., a tumor), demyelination, or ischemia. The syndrome is characterized by limitation of upward gaze, convergence retraction nystagmus, light near dissociation, and lid retraction (Collier's ... | Dorsal Mibrain Syndrome; Parinaud's Syndrome |
| 12 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Raed Behbehani, MD | Marcus Gunn Jaw Wink causes congenital ptosis and eyelid retraction associated with jaw movement or sucking. It's due to "miswiring" between 3rd and 5th cranial nerves. The treatment of ptosis in children is surgery to prevent amblyopia . | Jaw Winking; Marcus Gunn |
| 13 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks with Contrapulsion | Raed Behbehani, MD | A patient with history of brain stem stroke 2 months ago (right hemifacial anesthesia , left sided weakness and bulbar symptoms dysphagia) comes complaining of oscillipsia , binocular vertical diplopia). On exam he had a vertical tropia of 3-4 PD (Skew deviation), dissociated nystagmus , and saccadi... | Square Wave Jerks; Contrapulsion |
| 14 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor | Raed Behbehani, MD | This is a usually vertical, pendular nystagmus associated with synchronous rhythmic movement of the palate, developing months after a severe brain stem stroke. The stroke involves the dentato-rubro-olivary tract (Mollaret's triangle). MRI can show hypertrophy of the inferior olivary nucleus in the m... | Oculopalatal Tremor |
| 15 |
 |
Apraxia of Eyelid Opening | Raed Behbehani, MD | Patient has Parkinson disease and has developed this condition following deep brain stimulation. | Apraxia; Eyelid Opening |
| 16 |
 |
Pertinent Pupillary Problems | Karl C. Golnik, MD | Pupil Exam is a narrated PowerPoint that covers the basic of examining pupils. | Pupil Exam; Pupil |
| 17 |
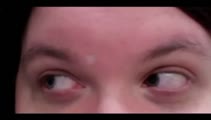 |
Bilateral Acquired Brown's Syndrome | Ryan D. Walsh, MD; Collin McClelland, MD | A 27 year old female with a history of Sjogren's syndrome reported a 2 year history of a vertical binocular diplopia with looking up-and-to-the right. She has also noticed an audible "click" when positioning her eyes in this direction. As depicted in the video, when attempting to look up-and-to-the... | Brown's syndrome; Brown syndrome; hypertropia; diplopia; disorder of ocular motility; Sjogren's syndrome |
| 18 |
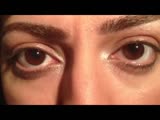 |
Downbeat Nystagmus Anti-GAD Cerebellar Syndrome | Raed Behbehani, MD | A patient with Anti-GAD positive Cerebellar syndrome with ataxia and opsoclonus due to downbeat nystagmus , treated with Baclofen with some improvement. | Downbeat Nystagmus |
| 19 |
 |
Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration | Raed Behbehani, MD | Optic nerve sheath fenestration is performed to manage papilledema causing progressive loss of vision , due to raised intracranial pressure from Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension or Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. The procedure is usually performed in cases of severe visual field loss or when m... | Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration |
| 20 |
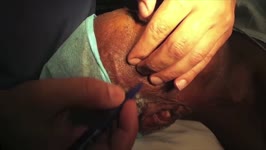 |
Temporal Artery Biopsy | Raed Behbehani, MD | This is a video of Superficial Temporal Artery Biopsy done under local anaesthesia for a patient who was suspected to have Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA. GCA is vasculitis of the medium sized vessels than can lead to permanent visual loss by causing Arteritis Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. The diagnosis of ... | Temporal Artery Biopsy; Giant Cell Arteritis |
| 21 |
 |
Pulsating Exophthalmos | Raed Behbehani, MD | This patient had brain surgery with bone removal resulted in transmission of CSF pulsation into the orbit and pulsating exophthalmos. This sign can also be seen in patient with neurofibromatosis with hypoplasia of the sphenoid wing bone. | Pulsating Exophthalmos; Neurofibromatosis |
| 22 |
 |
Anisocoria | Karl C. Golnik, MD | This is a narrated PowerPoint presentation that covers the common causes of anisocoria. | Pupil; Anisocoria |
| 23 |
 |
Cranial Nerves: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The approach is to learn to associate the cranial nerves with their brainstem level and blood supply. Emphasis is given to the midbrain (3, 4), pons (5, 6, 7, 8), medulla (9, 10, 11, 12) and their most important functions. | Cranial Nerves; Brain; Dissection |
| 24 |
 |
Hypothalamus: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | Gross specimens are used to demonstrate the area of the hypothalamus and its relationship to surrounding structures. Both endocrine and autonomic functions are explored using diagrams. Mention is made of the direct hypothalamic response to circulating hormones and other substances such as sodium. Th... | Hypothalamus; Brain; Dissection |
| 25 |
 |
Three Critical Vertical Pathways: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | There is one motor and two sensory pathways that must be mastered. Pain and temperature from the body travel together and vibration and proprioception travel in another pathway each reaching perception in the cortex. Voluntary motor control starts in the cerebral cortex and connects with a motor neu... | Spinothalamic Tract; Dorsal Column-Medical Lemniscus Pathway; Posterior Column; Vertical Pathway; Brain; Dissection |
