A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
6th Nerve Palsy as Initial Presentation of Metastatic Lung Cancer | A video describing 6th nerve palsy as initial presentation of metastatic lung cancer. | Image/MovingImage |
| 2 |
 |
A 'Canal Jam' During Head Impulse Testing in a Patient With Horizontal Canal BPPV | A 70-year-old man reported brief episodes of positional vertigo. Ten years prior, he had undergone gamma knife radiosurgery for a vestibular schwannoma at the left cerebellopontine angle. Video head impulse testing (vHIT) showed reduced gains and corrective saccades in the planes of the left horizon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 3 |
 |
A flowchart approach to nystagmus/intrusions | In tandem with the flowchart, the following added clues should be used to help with etiology: i) vector [horizontal, vertical, torsional]; ii) binocular or monocular; iii) spontaneous or provoked [e.g., BPPV]; iv) change with monocular viewing or gaze direction; v) rest of history, neurologic, and o... | Image/StillImage |
| 4 |
 |
Abnormal Active Head Impulse Testing Recorded Asynchronously in Bilateral Vestibular Loss | This is a video of patient with the subacute onset of head movement-dependent oscillopsia due to bilateral vestibular loss (with obvious bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) at the bedside), in addition to central ocular motor signs including saccadic smooth pursuit and gaze-evoked nystagmus... | Image/MovingImage |
| 5 |
 |
Abnormal Head Impulse Test in Vestibular Neuritis 1 Week After Onset | This is a 25-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome due to right-sided vestibular neuritis 1 week prior to this video. Left-beating nystagmus (LBN) was only noted in left gaze, but with fixation-removed, there was clear LBN in primary position that increased with head-shaking a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 6 |
 |
Acquired Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus Suppressed by Blinks and Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old man who experienced the gradual onset of oscillopsia over weeks about 3 months prior to this video recording. Examination demonstrated elliptical pendular nystagmus which was atypical for infantile n... | Image/MovingImage |
| 7 |
 |
Active Head Impulse Test | Active head impulse test (HIT): instruct the patient to fix their eyes on the camera and turn their head 20o to the right/left, and then make a rapid movement toward the midline to align their head with the camera again, keeping their eyes fixed on the camera throughout. A simple instruction is to a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 8 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Neuritis With Unidirectional Nystagmus and Abnormal Video Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is 45-year-old man who presented to the emergency department (ED) 2 days prior to this video recording with acute onset prolonged vertigo, nausea, head motion intolerance, unsteadiness and spontaneous nystagmus, cons... | Image/MovingImage |
| 9 |
 |
The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver (HC-Canalithiasis) | The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal-canalithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a supine position. 2. The patient rotates their head 90 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient sits up. | Text |
| 10 |
 |
The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver (HC-Canalithiasis) (Video) | The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal-canalithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a supine position. 2. The patient rotates their head 90 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient sits up. | Image/MovingImage |
| 11 |
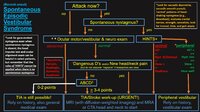 |
An Approach to the Patient with (Recent Onset) Spontaneous Episodic Vestibular Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the recent onset of the spontaneous (unprovoked) episodic vestibular syndrome (EVS), especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors ... | Image |
| 12 |
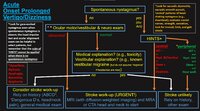 |
An Approach to the Patient with Acute Onset Prolonged Vertigo | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the acute onset prolonged vertigo, especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors are present. However, young patients can suffer fr... | Image |
| 13 |
 |
Apogeotropic and Downbeat Central Positional Nystagmus Provoked While Seated | This is a young man with intermittent complaints of positional vertigo. With Dix-Hallpike and roll testing, he had apogeotropic positional nystagmus (e.g., right beating nystagmus with the left ear down, and left beating nystagmus with the right ear down) in addition to strong downbeat nystagmus in... | Image/MovingImage |
| 14 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Image/MovingImage |
| 15 |
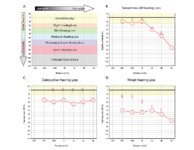 |
Audiometry: What Does It Look Like and How Do I Interpret It? | An audiogram measures a patient's auditory threshold responses with pure-tone stimuli across a range of sound frequencies that are important for human communication, typically 250 Hz to 8000 Hz. The threshold is the sound intensity level at which an individual detects the tone 50% of the time. Heari... | Text |
| 16 |
 |
Basics of Acute Stroke Treatment | A brief overview of management of acute stroke treatment. | Text |
| 17 |
 |
BBQ Roll for Right Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The BBQ Roll/Lampert Maneuver has been shown to be an effective treatment and is supported by a level I classification study. 1. The patient starts in a supine position with the head positioned 30 degrees above the horizon. 2. While maintaining head elevation, the patient's head (or whole body) is r... | Text |
| 18 |
 |
BBQ Roll for Right Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) (Video) | The BBQ Roll/Lampert Maneuver has been shown to be an effective treatment and is supported by a level I classification study. 1. The patient starts in a supine position with the head positioned 30 degrees above the horizon. 2. While maintaining head elevation, the patient's head (or whole body) is r... | Image/MovingImage |
| 19 |
 |
The Bedside Examination of the Ocular Motor System | A masterclass covering the bedside examination of the ocular motor system. | Image/MovingImage |
| 20 |
 |
Bilateral INOs Due to Stroke | This is a 65-year-old man with multiple vascular risk factors who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia 6 months prior to this video. MRI done within 24 hours of onset was unremarkable. Examination demonstrated subtle bilateral adduction lag with horizontal saccades. There was very mild abducting... | Image/MovingImage |
| 21 |
 |
Bilateral riMLF Syndrome Causing Vertical Saccadic Palsy and Loss of Ipsitorsional Fast Phases | This is a 60-year-old man who developed fatigue and diabetes insipidus about 12 months prior to this video, and MRI demonstrated hypothalamic enhancement at that time. Nine months prior to this video, he gradually noticed that he was unable to look down. Work-up for ischemic, infectious, inflammator... | Image/MovingImage |
| 22 |
 |
Bilateral Vestibular Loss With Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Saccadic Visually Enhanced VOR | This is 55-year-old man with the subacute onset of head movement-induced oscillopsia and dizziness. He had a history of psoriatic arthritis. He had not used medications known to be vestibulo-toxic such as gentamicin. ; Salient findings on his examination included 1) bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) d... | Image/MovingImage |
| 23 |
 |
Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) due to bilateral vestibular loss (BVL). Typical symptoms in BVL: head movement-induced dizziness and jumping vision for years with visual jumping/b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 24 |
 |
Bow and Lean Test | The Bow and Lean Test is used to identify the affected side and is designed to be used in conjunction with or after the Supine Roll Test. Within this test a null point may exist where the nystagmus will extinguish because the cupula is in a gravity neutral position. As this test involves the patient... | Text |
| 25 |
 |
Bow and Lean Test (Video) | The Bow and Lean Test is used to identify the affected side and is designed to be used in conjunction with or after the Supine Roll Test. Within this test a null point may exist where the nystagmus will extinguish because the cupula is in a gravity neutral position. As this test involves the patient... | Image/MovingImage |
