A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
1 - 25 of 11
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Anti-GAD Associated Cerebellopathy and Bilateral Vestibulopathy | This is a 70-year-old woman with the subacute onset of severe imbalance and dizziness. On her initial examination, she had prominent gaze-evoked nystagmus and bilateral vestibular loss. Smooth pursuit was saccadic, although her vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression was much smoother. Usually pur... | Abnormal Pursuit; Normal VORS; VOR Abnormal; HIT Abnormal; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus |
| 2 |
 |
Bilateral riMLF Syndrome Causing Vertical Saccadic Palsy and Loss of Ipsitorsional Fast Phases | This is a 60-year-old man who developed fatigue and diabetes insipidus about 12 months prior to this video, and MRI demonstrated hypothalamic enhancement at that time. Nine months prior to this video, he gradually noticed that he was unable to look down. Work-up for ischemic, infectious, inflammator... | Midbrain OMS; Downgaze Palsy; Upgaze Palsy; Vertical Gaze Palsy; Abnormal Saccades; Normal Pursuit |
| 3 |
 |
Caloric Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Caloric testing is a peripheral vestibular test which takes advantage of the fact that the labyrinth is sensitive to temperature changes. Warm stimulation causes excitation of the semicircular canals while cold stimulatio... | Normal VOR; Abnormal VOR; Vestibular Lab Testing; Calorics |
| 4 |
 |
HINTS Exam and Saccadic Dysmetria in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old who experienced the abrupt onset of prolonged vertigo following chiropractic therapy 2 months prior. Initial work-up included an MRI and MR angiogram - MR-diffusion weighted imaging showed an acute l... | Abnormal Saccades; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Normal VOR; Skew Deviation; OMS Medulla |
| 5 |
 |
Ipsitorsional Quick Phases with Head Tilt in a Normal Subject | This is a demonstration of ocular counterroll, which can be seen when the head is tilted to the right or to the left. For example, when the head is tilted to the right, the top poles of both eyes should rotate toward the left ear to keep the top poles oriented with earth vertical. This is part of ... | |
| 6 |
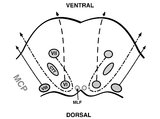 |
Pons: 6th, 7th, 8th, and Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomy | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th and 8th fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied by a + ipsilateral... | Sixth Nerve Palsy; OMS Pons; Facial Nerve; VOR Normal; VOR Abnormal |
| 7 |
 |
Rotary Chair Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Rotary chair testing includes rotation around a vertical axis, and evaluates the horizontal semicircular canal vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The patient sits in a mechanized chair with the head secured in a neutral posi... | Normal VOR; Abnormal VOR; Vestibular Lab Testing; Rotary Chair |
| 8 |
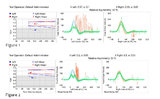 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Neuritis (Figures 1 and 2) | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | VOR Normal; VOR Abnormal |
| 9 |
 |
Using Video Head Impulse Testing to Unmask Covert Saccades in Compensated Vestibular Veuritis | This is a 30-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome (prolonged vertigo for >24 hours, nausea, unsteadiness, spontaneous nystagmus, head motion intolerance) and was diagnosed with vestibular neuritis. This diagnosis was based on a positive head impulse test to the left (see Figu... | VOR Normal; VOR Abnormal |
| 10 |
 |
VOR (Suppression) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Deficits in pursuit and vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)S usually go together, except when the VOR is absent or markedly diminished in which case there is no VOR to suppress, so that VORS seems better than pursuit. This is a... | Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (VOR) Supression; Exam |
| 11 |
 |
Video Head Impulse Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The video head impulse test (vHIT) is a clinical assessment technique used to assess the function of the semicircular canals-the angular acceleration detectors-which initiate the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The HIT and... | Normal VOR; Abnormal VOR; Vestibular Lab Testing; Video Head Impulse Testing |
1 - 25 of 11
