A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
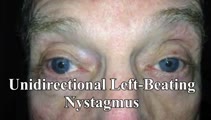 |
Unidirectional Vestibular Nystagmus | 60-yo-man with recurrent vertigo attacks - this video was taken during one of his typical attacks, and shows left-beating nystagmus that stayed left-beating in all directions of gaze, more in left gaze (in accordance with Alexander's Law), and less in right gaze. This pattern is more commonly seen w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 152 |
 |
Centripetal Nystagmus Example | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 153 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked, Rebound, and Centripetal Nystagmus in Cerebellar Degeneration | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 154 |
 |
Maddox Rod and Red Glass Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Describing the basics of strabismus. | Text |
| 155 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome in MS Due to Middle Cerebellar Peduncle/Root Entry Zone Lesion | This is a 13 year-old girl with relatively abrupt onset vertigo and oscillopsia. On exam, there was primarily right-beating nystagmus in primary gaze with a slight upward (upbeat) component, giving the nystagmus an oblique appearance. The upward component and lack of a clear torsional component acut... | Image/MovingImage |
| 156 |
 |
Apraclonidine Testing in Horner's syndrome | This patient experienced relatively abrupt ptosis and was seen and diagnosed with a Horner's syndrome within a few days of the onset. There were no other exam findings and history did not offer clues as to the etiology. Neuroimaging of the oculosympathetic tract was unrevealing. Apraclonidine testin... | Image/MovingImage |
| 157 |
 |
Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy and Oculopalatal Tremor Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This 70-yo-woman experienced headache and diplopia and was found to have a hemorrhage centrally within the dorsal pons. Months after the onset, the patient was seen in clinic and had no horizontal eye movements (pursuit, saccades, VOR) in either eye, suggestive of bilateral nuclear 6th nerve palsies... | Image/MovingImage |
| 158 |
 |
Cerebellar Degeneration with Downbeat Nystagmus Provoked by Convergence | Description: This is a 70-yo-woman with a progressive gait disorder, diagnosed with cerebellar ataxia. She displayed typical cerebellar ocular motor signs including gaze-evoked nystagmus, choppy pursuit and VOR suppression, and there was very subtle spontaneous downbeat nystagmus, best appreciated w... | Image/MovingImage |
| 159 |
 |
Chiari Malformation Causing Downbeat Nystagmus in Lateral Gaze | This is a 20-yo-man who presented with oscillopsia in lateral gaze from downbeat nystagmus (DBN). In primary gaze, very subtle DBN was only noted with ophthalmoscopy, but in lateral gaze, prominent DBN was present. Other central ocular motor signs included gaze-evoked nystagmus (GEN) vertically, in ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 160 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Atrophy | This is a 40-year-old man with 2 years of progressive ataxia and oscillopsia. On examination, he had downbeat nystagmus (DBN), an ocular motor finding that is usually (but not always) associated with flocculus/paraflocculus dysfunction, which causes overaction of the anterior canal (upward or anti-g... | Image/MovingImage |
| 161 |
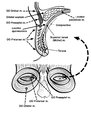 |
Eyelid Anatomy | Seen here are the major muscles of eyelid opening and closure. The levator palpebrae, which is innervated by the oculomotor nerve, inserts on the tarsus via the levator aponeurosis and directly on the skin of the upper eyelid. The superior tarsal muscle (also known as Muller's muscle, which is inner... | Image |
| 162 |
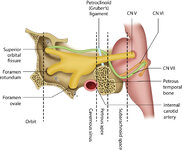 |
Figure 46: The Course of the 6th (VI) Nerve | The sixth nucleus is located dorsally, adjacent to the 4th ventricle, in the lower pons. The genu of the facial (7th) nerve wraps around the 6th nucleus, creating the facial colliculus, which bulges into the 4th ventricle. After the 6th nerve leaves the pons, it follows a vertical course along the c... | Image |
| 163 |
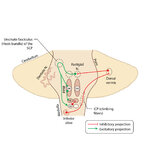 |
Figure 50: Anatomy and Physiology of the Saccadic Pathways | When a saccade is desired (or reflexively triggered), signals project from the saccade-related cortical eye fields to the superior colliculus, which serves to integrate and relay commands to the saccade generating brainstem circuitry. The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to... | Image |
| 164 |
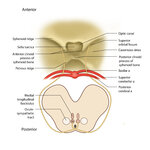 |
Figure 68: The Course of the 4th (IV) Nerve | The 4th nucleus lies at the ventral border of the periaqueductal gray matter, at the level of the inferior colliculus. The fascicles exit the nucleus dorsally and decussate at the anterior medullary velum (anterior floor of the fourth ventricle), and then exit the brainstem dorsally. The peripheral ... | Image |
| 165 |
 |
Five Common Ocular Motor Signs in Cerebellar Disorders - Saccadic Hypermetria, Saccadic Pursuit & VOR Suppression, Gaze-evoked & Rebound Nystagmus | (1) Saccadic hypermetria - an overshoot of the visual target (2) Saccadic smooth pursuit - due to impaired pursuit and low gain, saccades are needed to keep up with the visual target. This gives it a ‘choppy' appearance. (3) Saccadic vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression - another... | Image/MovingImage |
| 166 |
 |
Head Movement Independent ('Sitting') Oscillopsia - A Common Symptom of Nystagmus and Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video is an example of what a patient with spontaneous nystagmus or saccadic intrusions/oscillations experiences visually during the abnormal eye movements - i.e., oscillopsia (illusion of movement of the stationary ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 167 |
 |
Horner's Syndrome with Anhidrosis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with the onset of ptosis OD years prior, with clear evidence of a Horner's syndrome. Imaging of the oculosympathetic tract was unrevealing. The patient also mentioned that with exercise, the left side of... | Image/MovingImage |
| 168 |
 |
Idiopathic Downbeat Nystagmus, Decreasing with Convergence | This is a 25-yo-woman who experienced vertically oscillopsia for 1 year, and was found to have downbeat nystagmus. Interestingly, there were no other cerebellar ocular motor signs - e.g., normal saccades, smooth pursuit, VOR suppression, and no gaze-evoked nystagmus, although her (pure) downbeat was... | Image/MovingImage |
| 169 |
 |
Ipsitorsional Quick Phases with Head Tilt in a Normal Subject | This is a demonstration of ocular counterroll, which can be seen when the head is tilted to the right or to the left. For example, when the head is tilted to the right, the top poles of both eyes should rotate toward the left ear to keep the top poles oriented with earth vertical. This is part of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 170 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus and DVD in Infantile Esotropia | This is a 20-year-old woman with infantile esotropia (s/p strabismus surgery as a child) who demonstrated latent nystagmus and presumed dissociated vertical deviation (DVD) OS, which are commonly seen with infantile esotropia (also inferior oblique overaction and monocular nasotemporal asymmetry to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 171 |
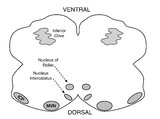 |
Medullary Structures Relevant to Upbeat Nystagmus | This is an axial section of the medulla, slightly more caudal as compared to (please refer to figure "medullary structures relevant to the ocular motor and vestibular consequences of the lateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome). Again seen are the inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) and caudal aspect... | Image |
| 172 |
 |
Mild 6th Nerve Palsy Due to Pontine Stroke | This is a 70-year-old woman with HTN and diabetes who presented with horizontal diplopia for several weeks, worse in right gaze. There was a very subtle abduction paresis OD with full motility elsewhere. With cover-uncover testing, there was a small esotropia in right gaze (esodeviation seen with al... | Image/MovingImage |
| 173 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome, Facial Palsy, and Nystagmus Due to Dorsal Pontine Demyelination | This is a 16-yo-girl with oscillopsia and double vision. Exam showed inability to look to the left with either eye due to left nuclear 6th. There was also a left INO (horizontal gaze palsy + INO = one-and-a-half syndrome) from left MLF involvement and left lower motor neuron facial palsy due to fasc... | Image/MovingImage |
| 174 |
 |
Oscillopsia and Bilateral Vestibular Loss with Gentamicin Ototoxicity | Patients with bilateral vestibular loss commonly experience oscillopsia with head movements, or an inability to stabilize retinal images with subsequent bouncing or jumping of the environment due to loss of vestibular function. This causes significant blurring of vision and disorientation, dizziness... | Image/MovingImage |
| 175 |
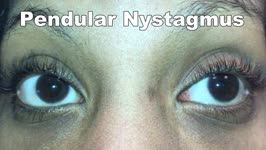 |
Pendular Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is an example of pendular nystagmus, where like jerk nystagmus, the slow phase initiates the movement. However, unlike jerk nystagmus, there is no fast phase, but rather back to back slow phases resembling a pendulum... | Image/MovingImage |
