A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
 |
Skew Deviation and the Triad of the Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) | This is a patient who presented with vertical diplopia, who was found to have a complete ocular tilt reaction including the following features: (1) Skew deviation - right hypertropia that was about 30 prism diopters in all directions of gaze including right, left, up, down, as well as in right and ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 127 |
 |
Slow Horizontal, Vertical and Oblique Saccades in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type I | This is a patient presenting with horizontal diplopia who was found to have divergence insufficiency, an esotropia greater at distance than near in the absence of abduction paresis. She also had very slow saccades, more so vertically than horizontally. This is particularly noticeable when asking h... | Image/MovingImage |
| 128 |
 |
Slow Horizontal, Vertical, Oblique Saccades and Gaze-evoked Nystagmus in Anti-AGNA-1 Encephalitis | This is a patient who presented subacutely with imbalance and dizziness. On examination, she had evidence of gaze evoked nystagmus, right internuclear ophthalmoplegia, as well as slow saccades horizontally and vertically. She was diagnosed with a rare antibody-mediated disorder, anti-AGNA-1 (antig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 129 |
 |
Smooth Pursuit | Smooth pursuit: instruct the patient to hold their head steady, fix their eyes on the camera and slowly move the camera in the horizontal and vertical planes. Or, have the patient focus on their outstretched thumbnail (or other small fixation target), while following the slowly moving object horizon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 130 |
 |
Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3 with Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Bilateral Vestibular Loss | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with an established diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA 3) with severe imbalance and head movement-induced oscillopsia. On examination, she had 1) bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) de... | Image/MovingImage |
| 131 |
 |
Spontaneous Torsional Nystagmus and Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old man who experienced "a delay in focusing" with "some twisting movement" that began about 18 months prior to this video with mild progression over days or weeks. For the same period of time, he experi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 132 |
 |
Square Wave Maneuver for Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal BPPV | The square wave maneuver is designed to treat individuals with horizontal canal cupulolithaisis and is commonly used when individuals have cervical restrictions and the affected side is not well identified at baseline. 1. The patient begins in the supine position with the head 20 to 30 degrees above... | Text |
| 133 |
 |
Square Wave Maneuver for Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal BPPV (Video) | The square wave maneuver is designed to treat individuals with horizontal canal cupulolithaisis and is commonly used when individuals have cervical restrictions and the affected side is not well identified at baseline. 1. The patient begins in the supine position with the head 20 to 30 degrees above... | Image/MovingImage |
| 134 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia - Three Patients with Recorded Attacks Using VOG and Frenzel Goggles | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Patients with superior oblique myokymia (SOM) commonly present with complaints of monocular oscillopsia and/or vertical diplopia, which are related to the primary and secondary actions of the SO (incycloduction and depres... | Image/MovingImage |
| 135 |
 |
Supine Head-Hanging Test | The supine head-hanging test is more sensitive for AC-BPPV, but it does not differentiate laterality, as both canals are stimulated at the same time [1-3]. When the individual returns to a seated position, the otoconia should hypothetically move closer to the utricle, which continues their ampullofu... | Text |
| 136 |
 |
Supine Head-Hanging Test (Video) | The supine head-hanging test is more sensitive for AC-BPPV, but it does not differentiate laterality, as both canals are stimulated at the same time [1-3]. When the individual returns to a seated position, the otoconia should hypothetically move closer to the utricle, which continues their ampullofu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 137 |
 |
Supine Roll Test | Supine roll test: used to test for horizontal canal (HC) BPPV. While horizontal nystagmus due to HC-BPPV is often seen with DH, the roll test will usually maximize nystagmus and vertigo with the HC variant. The patient can be guided through a self-administered supine roll test while lying on the flo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 138 |
 |
Supine Roll Test/Pagnini-McClure Test | The supine roll test or the Pagnini-McClure Test is used to assess for horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. Apogetropic nystagmus is indicative of cupulolithias... | Text |
| 139 |
 |
Supine Roll Test/Pagnini-McClure Test (Video) | The supine roll test or the Pagnini-McClure Test is used to assess for horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. Apogetropic nystagmus is indicative of cupulolithias... | Image/MovingImage |
| 140 |
 |
Test of Latency | The Test of Latency is used to identify which side is involved for patients with horizontal canal BPPV and is used in conjunction with the Supine Roll Test. For canalithiasis, lateralization is considered the side with a shorter latency time. For cupulolithasis, lateralization is considered the side... | Text |
| 141 |
 |
Test of Latency (Video) | The Test of Latency is used to identify which side is involved for patients with horizontal canal BPPV and is used in conjunction with the Supine Roll Test. For canalithiasis, lateralization is considered the side with a shorter latency time. For cupulolithasis, lateralization is considered the side... | Image/MovingImage |
| 142 |
 |
Third and Sixth Nerve Palsies Due to Cavernous Sinus Meningioma | This is a 60-year-old woman with a large meningioma that was compressing the right cavernous sinus. Examination demonstrated a pupil-involving right 3rd nerve palsy with near complete external ophthalmoplegia (involving levator palpebrae, medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus). There was a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 143 |
 |
Third Nerve Palsy Due to Tolosa Hunt Syndrome | This is a 20-year-old woman presenting with severe left eye pain and diplopia for several days. Examination was consistent with a pupil sparing left 3rd nerve palsy with complete external ophthalmoplegia (involving levator palpebrae, medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus). Abduction OS was... | Image/MovingImage |
| 144 |
 |
Unidirectional Nystagmus Two Days After Onset of Vestibular Neuritis | Image/MovingImage | |
| 145 |
 |
Upbeat Nystagmus & Ocular Flutter Due to Cerebellar Pilocytic Astrocytoma | This is a 20-year-old woman who was diagnosed with a cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma at age 10 after presenting with severe headaches and hydrocephalus. She underwent incomplete resection and radiation therapy at that time. She experienced mild vertical oscillopsia in upgaze at baseline, and increa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 146 |
 |
Upbeat Transitioning to Downbeat Nystagmus in Wernicke's Encephalopathy | This is a 30-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse who presented to the hospital with inability to walk after several weeks of heavy drinking and malnutrition. While in the hospital, he noted that when he would look straight ahead, everything he saw would appear to be bouncing up and down - a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 147 |
 |
Valsalva (Closed Glottis) | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 148 |
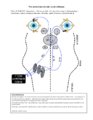 |
Vertical Semicircular Canal Pathways | Anterior Canal Pathway Afferents that originate in the anterior canals (AC) of the peripheral labyrinth first synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus. Three pathways exist: 1) medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) - right AC afferents to right medial vestibular nucleus (MVN), decussate and asc... | Image |
| 149 |
 |
Vestibulocerebellum Lecture | A lecture on vestibulocerebellum. | Image/MovingImage |
| 150 |
 |
Vibration | Vibration: instruct the patient to self-administer this test with an electric toothbrush or vibrator/massager, if available. Vibration of the mastoids and vertex will induce an ipsilesional slow phase with unilateral vestibular loss (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1427582). | Image/MovingImage |
