A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Text |
| 27 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises (Video) | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 28 |
 |
Bruns Nystagmus (During Video-Oculography) Due to Vestibular Schwannoma | A 25-year-old man with a history of right-sided hearing loss, headaches and imbalance was found to have a right vestibular schwannoma on MRI, and underwent a partial resection and radiotherapy. He denied symptoms of head movement dependent oscillopsia (i.e., suggestive of significant unilateral or b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Text |
| 30 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Video) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Image/MovingImage |
| 31 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
Central Vestibular Nystagmus in Anti-DPPX Encephalitis | This is a young woman who presented with oscillopsia due to spontaneous nystagmus in addition to gastrointestinal symptoms which led to the diagnosis of anti-DPP axis encephalitis. She was treated with rituximab, and experience gradual improvement over time. However, years after the onset, she con... | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
 |
Centripetal Nystagmus Example | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
Change in Pendular Nystagmus from Oculopalatal Tremor over a Four-year Period | This is a patient who developed oculopalatal tremor months following a pontine hemorrhage. Although it is not shown here, she also has palatal tremor. In the first video which was taken 1 year after her hemorrhage, a vertical-torsional pendular nystagmus can be seen, that is mildly dissociated giv... | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
 |
Chronic Facial Nerve Palsy with Aberrant Regeneration | This is a 35-year-old woman who was diagnosed with right sided Bell's palsy six months prior. Contrast-enhanced MRI at that time was normal. This video demonstrates the phenomenon of aberrant regeneration (synkinesia) of the facial nerve. Due to aberrant regeneration, at rest the right palpebral fi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
Common Neuro-Ophthalmic Ancillary Tests to Assist in the Diagnosis and Localization of Afferent Disorders | Chart of the common neuro-ophthalmic ancillary tests to assist in the diagnosis and localization of afferent disorders. | Text |
| 37 |
 |
Complete Saccadic Palsy Due to Pulmonary Thrombectomy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 37-year-old woman who underwent pulmonary thrombectomy for a pulmonary embolus. Immediately following the procedure, she was unable to make normal eye movements. This video exam (she is the passenger in a car du... | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Convergence | Convergence: instruct the patient to focus on their thumb held at arm's length, and slowly move their thumb towards their nose. This may bring out or cause reversal of vertical nystagmus (e.g., transition from upbeat to downbeat nystagmus in Wernicke's encephalopathy [see example of transition from ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Curved Oblique Saccades and Saccadic Slowing in a Patient with an Anti-GAD Mediated Posterior Fossa Syndrome | This is a patient who developed muscle spasms especially involving the muscles of the trunk in addition to a progressive gait disorder. Examination demonstrated slow saccades, slower horizontally than vertically, in addition to gaze evoked nystagmus with a side pocket pattern. Side pocket nystagmu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
Dissociated Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus in MS | This is a patient with multiple sclerosis who presented with oscillopsia. Seen in the video is an elliptical pendular nystagmus in both eyes that was dissociated. Here, the term "dissociated" refers to the fact that the nystagmus is (slightly) more intense in the left eye as compared to the right ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike | The safety of the patient should be prioritized when completing this test virtually, and the examiner should avoid putting the patient in a position where a fall may occur. Floor (or bed) Dix-Hallpike: this test can be used for patients who are fully mobile and able to get down to the floor and up a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
 |
Downbeat (Perverted) Head Shaking Nystagmus in a Patient with Spontaneous Torsional Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with vascular risk factors who experienced abrupt onset imbalance and dizziness. Symptoms were maximal at onset, and she denied progression over 6 months. Clinically, it was felt that she had s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus with Active Horizontal Head Shaking | This is a 70-year-old man who presented with one single complaint for 10 years - if he moved his head too quickly (even one single horizontal head movement to the right or the left), he would experience the abrupt loss of balance and dizziness. His typical episodes were reproducible, and interesting... | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | Dynamic Visual Acuity: the examiner can use screen-sharing to provide a visual acuity chart. Instruct the patient to sit at the appropriate distance from their screen at which the lowest line on the visual acuity chart is just readable. Have the patient move their head (horizontally to evaluate the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Expanded Nystagmus & Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations Differential | Expanded nystagmus & saccadic intrusions/ oscillations differential | Text |
| 46 |
 |
Eye Handbook App for OKN | Optokinetic nystagmus (OKN): one way this can be examined virtually is using a smartphone application (e.g. Eye Handbook © app used in this video) or optokinetic tape/flag/drum held in front of the examiner's camera. The optokinetic stimulus should occupy the full screen of the patient's device (ea... | Image/MovingImage |
| 47 |
 |
Eyelid Nystagmus | Lid nystagmus is a rhythmic eyelid movement commonly seen as an epiphenomenon of vertical nystagmus (typically upbeating, as in this case) due to a shared central pathway controlling elevation of the lid and supraduction. There can be isolated lid nystagmus if there is accompanying impairment of su... | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
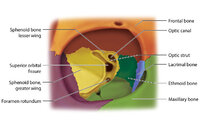 |
Figure 17: Bony Structures Relevant to the Orbit | The frontal, sphenoid, maxillary, ethmoid, and lacrimal bones make up the orbit. Structures passing through the optic canal include the optic nerve, oculosympathetic tract and ophthalmic artery. Structures passing through the superior orbital fissure include the superior ophthalmic vein, cranial ner... | Image |
| 49 |
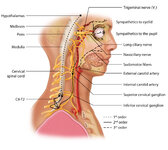 |
Figure 1: Oculosympathetic Pathway for Pupillary Dilation | The oculosympathetic tract is an uncrossed pathway that begins in the hypothalamus, with fibers descending in the brainstem (1st order, commonly affected in a lateral medullary syndrome), synapsing in the lower cervical/upper thoracic spinal cord (interomediolateral cell columns of C8-T2, also refer... | Image |
| 50 |
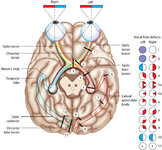 |
Figure 24: Typical Visual Field Defects Associated with Discrete Lesions Along the Visual Pathways | Specific monocular or binocular visual field defects can be highly localizing when the neuroanatomy of the visual pathways is understood. The temporal visual field corresponds to the nasal retina, while the nasal visual field corresponds to the temporal retina. 1) Left optic nerve lesion - while an ... | Image |
