A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 |
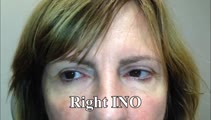 |
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (INO) in Multiple Sclerosis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This video includes 3 patients each with a known history of MS found to have unilateral or bilateral INOs on their exam. In the first 2 patients, the INOs are relatively subtle with normal adduction. However, with rapid h... | Image/MovingImage |
| 227 |
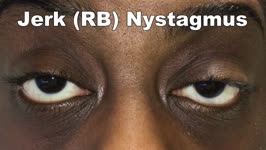 |
Jerk Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is an example of jerk nystagmus due to a central vestibular lesion. The slow phase is the pathologic phase (to the left) which initiates the movement, and is followed by a fast position reset mechanism (to the right)... | Image/MovingImage |
| 228 |
 |
Light Near Dissociation in a Tonic Pupil | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman who noticed difficulty reading and heightened sensitivity to lights OS for the last 6 months. On examination, there was mydriasis OS of about 6 mm (3 mm OD). The left (mydriatic) pupil constric... | Image/MovingImage |
| 229 |
 |
Nystagmus Due to Paraneoplastic (Anti-Yo) Brainstem and Cerebellar Degeneration | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-woman with anti-Yo antibody associated with ovarian cancer. Initial symptoms 2.5 years prior (to this video) included imbalance and dysarthria. She complained of oscillopsia which was due to her upbeat nys... | Image/MovingImage |
| 230 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman complaining of imbalance and double vision. She had significant convergence insufficiency (and would close her right eye with near viewing), providing an explanation for her diplopia. Convergence ins... | Image/MovingImage |
| 231 |
 |
Positional Downbeat Nystagmus Mimicking Anterior Canal BPPV | Although positional downbeat nystagmus (pDBN) can indicate the rare anterior canal variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, central mimics are common causes of pDBN. pDBN may be seen in multiple system atrophy (MSA), or seen with posterior fossa lesions, with a common example being a stroke ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 232 |
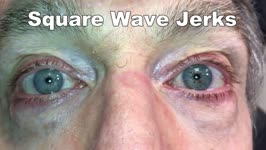 |
Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks, SWJ) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are SWJ, which is the most common example of a saccadic intrusion. Here the patient is fixating on the camera, and all of the sudden a saccade takes the eyes off the fixation target, there's a brief intersaccadi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 233 |
 |
Saccadic Smooth Pursuit and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex Suppression (VORS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 20-yo-man who suffered a left MCA stroke years prior. Upon evaluation of his eye movements, saccades and all classes of eye movements were normal, although his smooth pursuit and VORS were choppy to the left (ip... | Image/MovingImage |
| 234 |
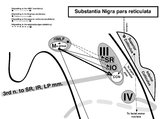 |
Sagittal Section of the Midbrain Showing Structures Related to Normal Eyelid Function | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: During a vertical saccade, the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF) is activated, which excites the superior rectus (SR) and inferior oblique (IO) (IIIrd nerve) subnuclei. Additionall... | Image |
| 235 |
 |
Sitting & Walking Oscillopsia in a Patient with Bilateral Vestibular Loss & Head Tremor | This is a 55-year-old man with oscillopsia for two reasons: He experienced oscillopsia at rest - so-called ‘sitting' oscillopsia - not from spontaneous nystagmus, but because of a combination of bilateral vestibular loss (BVL) and a mainly horizontal head tremor (this is sometimes referred to a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 236 |
 |
Torsional Jerk Nystagmus | Presented here are 3 patients with torsional jerk nystagmus. The first patient presented with vertigo and experienced oscillopsia due to her torsional nystagmus. Pure or predominantly torsional nystagmus is highly suggestive of a central process. Her nystagmus was unidirectional and followed Alexand... | Image/MovingImage |
| 237 |
 |
Typical Features of Duane Syndrome Type 1 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient seen for vestibular complaints, who on exam, was found to have (unrelated to her vestibular symptoms) impaired abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of glo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 238 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Image/MovingImage |
| 239 |
 |
Peripheral (Vestibular) and Central (Gaze-Evoked) Patterns of Nystagmus in a Single Patient | A 55-year-old man experienced episodic vertigo and was diagnosed with Meniere's disease affecting the left ear (based on audiograms and his clinical course) about 1 year prior to presentation. About 6 months prior to presentation, intratympanic (IT) gentamicin was injected into the left ear, at whic... | Image/MovingImage |
| 240 |
 |
Anti-GAD Associated Cerebellopathy and Bilateral Vestibulopathy | This is a 70-year-old woman with the subacute onset of severe imbalance and dizziness. On her initial examination, she had prominent gaze-evoked nystagmus and bilateral vestibular loss. Smooth pursuit was saccadic, although her vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression was much smoother. Usually pur... | Image/MovingImage |
| 241 |
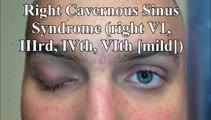 |
Cavernous Sinus Mass Causing Right 3rd and 4th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 25-yo-man who complained of diplopia and was initially found to have right 4th and 6th nerve palsies in the setting of a right cavernous sinus mass (subsequently diagnosed as Ewing's sarcoma). When seen in follow-up (this... | Image/MovingImage |
| 242 |
 |
Central (Nuclear) 3rd Nerve Palsies | Shown here are two patients with left sided midbrain pathology (hemorrhage and ischemia) which caused damage to the 3rd nucleus. Both of the patients have ipsilateral mydriasis, adduction, supra- and infraduction paresis. Ipsilateral>contralateral ptosis is also present, and localizes to the central... | Image/MovingImage |
| 243 |
 |
Complete Peripheral Vestibulopathy & Ipsilateral Facial Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 60-yo-man who suffered the fairly abrupt onset (over hours) of right lower motor neuron facial nerve palsy (7th cranial nerve), vertigo and deafness in the right ear (8th cranial nerve). Vesicles were noted on otoscopy, a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 244 |
 |
Divergence Insufficiency in Cerebellar Ataxia | This is a 65-yo woman with complaints of imbalance (progressive over years) and horizontal diplopia at distance. On her exam, there was a small symptomatic esotropia at distance, but only a small esophoria at near. There were no obvious abduction deficits, and the 6 prism diopter ET at distance was... | Image/MovingImage |
| 245 |
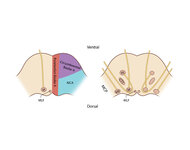 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons | In this axial section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th (VII) and 8th (VIII) fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery, AICA territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied b... | Image |
| 246 |
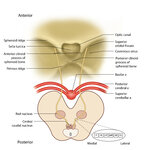 |
Figure 64: The Course of the 3rd (III) Nerve | The 3rd nucleus lies at the ventral border of the periaqueductal gray matter, at the level of the superior colliculus. In between the two nuclei is the midline central caudal nucleus (CCN), which innervates bilateral levator palpebrae muscles (explaining how a unilateral nuclear 3rd can cause bilate... | Image |
| 247 |
 |
Leukemic Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Causing 4th and 6th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-yo-man with CML that recurred as AML. Diagonal diplopia developed, and on examination he was found to have a partial right 6th nerve palsy, in addition to a left hypertropia that increased in right gaze, down... | Image/MovingImage |
| 248 |
 |
Medial Medullary Syndromes | This is a video of two patients who suffered small strokes involving the right medial medulla, and who presented with acute vertigo and oscillopsia. The first patient in the video had pure upbeat nystagmus, while the second patient had upbeat-torsional (towards the right ear) nystagmus in addition t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 249 |
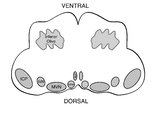 |
Medullary Structures Relevant to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular Consequences of Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | This is an axial section of the medulla showing the structures that, when damaged, are responsible for the vestibular and ocular motor features of the lateral medullary or Wallenberg syndrome. The nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH) and medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) complex is important for horizo... | Image |
| 250 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in SCA 6 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 45-yo-man who was recently diagnosed with SCA 6. There was no clear spontaneous downbeat nystagmus (DBN) in primary gaze, although DBN could clearly be provoked by convergence. Other ocular motor features includ... | Image/MovingImage |
