AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_aao_nanos"
1 - 25 of 17
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
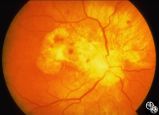 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Papilledema may produce visual loss due to chronic atrophic papilledema, secondary macular hemorrhage, exudate or edema, secondary ischemic optic neuropathy, or secondary subretinal neovascular membrane formation. Patients with papilledema and visual loss should be suspected of harboring one of thes... |
| 2 |
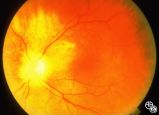 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Mark J. Kupersmith, MD | Papilledema may produce visual loss due to chronic atrophic papilledema, secondary macular hemorrhage, exudate or edema, secondary ischemic optic neuropathy, or secondary subretinal neovascular membrane formation. Patients with papilledema and visual loss should be suspected of harboring one of thes... |
| 3 |
 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Michael Wall, MD | This 36-year-old man noticed blurry vision in his right eye when attempting to sight a gun. He also reported bifrontal headaches responsive to aspirin. Acuity was 20/50 OD, 20/13 OS. His right eye could be refracted to 20/20 with a +2.50 sphere. A 0.3 right relative afferent pupillary defect was pre... |
| 4 |
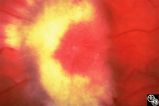 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 48-year-old man presented with a 1-month history of headache. Both discs had the appearance seen in this image, with prominent peripapillary nerve fiber layer myelination; the disc itself is hyperemic, with dilated, telangiectatic surface vasculature, suggesting true disc edema as well. |
| 5 |
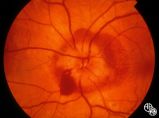 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Richard H. Legge, MD | Papilledema is a term reserved for optic disc edema related to increased intracranial pressure (eg. Papilledema, sixth nerve palsy, headache), a normal neuroimaging study, and an elevated opening pressure with normal cerebrospinal fluid contents. |
| 6 |
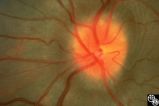 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This image demonstrates Paton's lines in a 34-year-old patient with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema. |
| 7 |
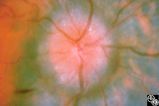 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can be seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image shows the chronic papilledema at presentation, with associated refractile hyaline bodies at the disc periphery in both eyes. Pair with 96... |
| 8 |
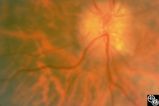 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can be seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image shows the chronic papilledema at presentation, with associated refractile hyaline bodies at the disc periphery in both eyes. Pair with 96... |
| 9 |
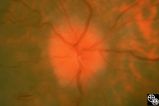 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can been seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image exhibits decreased disc edema and resolution of the refractile bodies OD after therapy. Pair with 96_01, 96_02, 96_04, 96_05, and 96_06... |
| 10 |
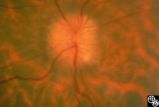 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can be seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image exhibits decreased disc edema and resolution of the refractile bodies OD after therapy. Pair with 96_01, 96_02, 96_03, 96_05, and 96_06. |
| 11 |
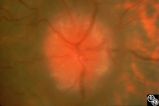 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can been seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image demonstrates later recurrence of the refractile bodies with worsening papilledema OD. Pair with 96_01, 96_02, 96_03, 96_04, and 96_06. |
| 12 |
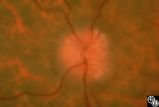 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Anthony C. Arnold, MD | This 42-year-old male with pseudotumor cerebri and chronic papilledema demonstrated refractile bodies, which can be seen with chronic optic disc edema. This image demonstrates later recurrence of the refractile bodies with worsening papilledema OD. Pair with 96_01, 96_02, 96_03, 96_04, and 96_05. |
| 13 |
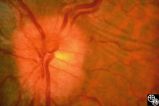 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema in pseudotumor cerebri may result in adjacent choroidal or retinal folds. |
| 14 |
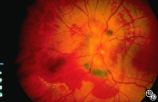 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema may produce visual loss due to chronic atrophic papilledema, secondary macular hemorrhage, exudate or edema, secondary ischemic optic neuropathy, or secondary subretinal neovascular membrane formation. |
| 15 |
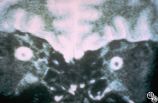 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema is a term reserved for optic disc edema related to increased intracranial pressure. Fluid within the optic nerve sheath or elevation of the intraocular optic nerve head may be visible on magnetic resonance imaging studies of the head and orbit. |
| 16 |
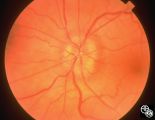 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Ralph A. Sawyer, MD | Papilledema usually results in bilateral optic disc edema without visual loss. The blind spot may enlarge initially, but progressive visual field loss may occur with chronic optic disc edema. Asymmetric or frankly unilateral optic disc edema may occur due to structural disc fractures that prevent th... |
| 17 |
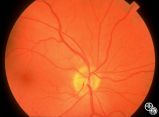 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Ralph A. Sawyer, MD | Papilledema usually results in bilateral optic disc edema without visual loss. The blind spot may enlarge initially, but progressive visual field loss may occur with chronic optic disc edema. Asymmetric or frankly unilateral optic disc edema may occur due to structural disc fractures that prevent th... |
1 - 25 of 17
