The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
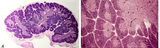 |
Thymus (human, newborn, low and higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabeculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a l... | Zhen; thymus cortex; thymus medulla; Hassall's corpuscle ; Lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 2 |
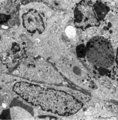 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitating dendritic cells (1) (so-called antigen-presenting cell, APC) exhibit numerous slender cell projections (1). (2) shows a macrophage with large lysosomes with heterogeneous contents. Small elongated fibroblastic reticular cells (3) form a structural framework ... | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 3 |
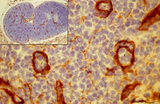 |
Immunohistochemistry of laminin in cortex lymph node (rat) | Anti-laminin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes (BM) are outlined demonstrating postcapillary venules (1) in the paracortical areas, as well as larger b... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); laminin; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 4 |
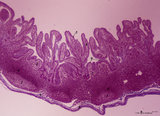 |
Ileum with Peyer's patches ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the ileum and called 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' (GALT). These so-c... | follicle; lymph node; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 5 |
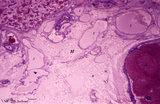 |
Hilum side of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Site of the hilum of a lymph node includes part of the medulla and medullary cords (1) and medullar sinuses (2). In the hilum (H) dilated efferent lymphatic vessels (3) and draining veins (4) and entering arteries (5) are present. (6) represents adipose tissue embedding the efferent ves... | hilum; lymphatic vessels; medullary cords; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 6 |
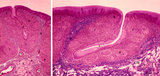 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Survey; B: detail of the crypt. The lingual tonsil consists of accumulations of bulging lingual lymphatic follicles in the dorsal part of the tongue behind the terminal sulcus, and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. The left (A) and right (B) ... | lingual tonsil; GALT; Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; crypt | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 7 |
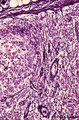 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia of reticular fibres the reticular network is black-stained among others such as collagen type I, III, IV. From the fibrous capsule (1) a meshwork of fine reticular fibres penetrates into the cortex of a lymph node crossing the subcapsular (or m... | germinal center; argyrophilia; reticular fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 8 |
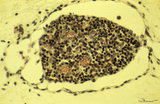 |
Lymph node (fetus, human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Along the course of lymphatic vessels lymph nodes develop. Lymphatic vessels dilate and form lymphatic sacs and lymphocytes aggregate around these sacs. A tiny developing lymph node with dense-stained thymocyte nuclei is closely associated with dilated lymph capillaries. ... | fetal lymph node; development | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 9 |
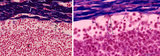 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left: subcapsular (or marginal) sinus in lymph node. Right: higher magnification. Both pictures show a thick capsule (1), at (2) subcapsular (or marginal) sinus filled with lymphocytes indicate (lining) littoral cells (?). Reticular cells (3) are localized perpendicularly through sin... | subcapsular sinus; reticular cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 10 |
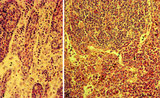 |
Lymph nodes (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & pyronin. Pyronin was formerly used to demonstrate young blast cell types rich in polysomes and packed rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) resulting in a reddish stain of the cytoplasm. A: Part of the medulla with medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum o... | infection; medullar cord; plasma cells ; macrophages | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 11 |
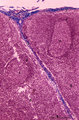 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. From the blue-stained dense capsule a long trabecula (3) flanked by paratrabecular (intermediate) sinuses penetrates between the paracortical areas (6). Paratrabecula... | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset | |
| 12 |
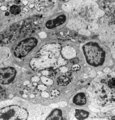 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. In the paracortical area (inner cortex) of a lymph node interdigitating cells (1) are found (so-called IDC, antigen-presenting cell or APC). They show branched extensions (3) in between the closely apposed surrounding T lymphocytes (2). In the cytoplasm of the IDC lysosomal inc... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 13 |
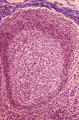 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Below the subcapsular sinus a darkly stained rim or corona (3) of small lymphocytes (B cells) surrounds the lucid stained germinal centre (4). The white spaces repre... | follicle; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 14 |
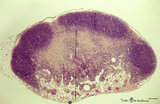 |
Lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. For comparison with the human lymph node a survey of a small rodent lymph node is demonstrated. Basically the same divisions are found: (1) a cortex (outer cortex zone, nodular cortex or superficial cortex) covered with a (2) thin capsule and subcapsular sinus; a paracor... | follicle; hilum; medulla; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 15 |
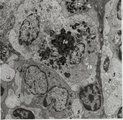 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. Within the reticular framework of lymph nodes a variety of active reticular cells are present, some of them (1) have phagocytised foreign material (1a) and contain numerous lysosomal structures (1a) and large Golgi areas (1b)). Others are less active (2). (3) wandering interdig... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 16 |
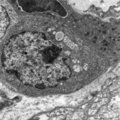 |
Lymphoblast in splenic cord of red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. A free circulating more matured lymphoblast with a conspicuous nucleus and nucleolus (1) still contains many polysomes (2), the swollen mitochondria (3) are obvious. A single fat droplet (4) and Golgi vesicles (5) are present. The cell is partly surrounded by reticular cell exte... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 17 |
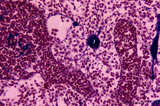 |
Medullary part of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla with darkly stained medullary cords (1) and lightly stained medullary sinuses (2). The cords are stuffed with densely packed lymphocytes and reticular cells. Their blue-stained structures indicate massive bundles of reticular fibres. The sinuses are lined by flattene... | medulla; medullar cords; sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 18 |
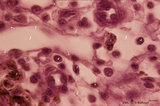 |
Medullary cords and sinus in lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Detail of medullary sinus (1) flanked by part of medullar cords (2). The sinus space (1) is lined by flattened littoral cells (foamed cytoplasm) (?) and dispersedly filled with lymphocytes (4) and macrophages (brown hemo-pigment) (3). Within the medullary cords one finds ... | medullar cords; medullar sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 19 |
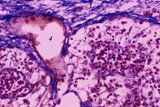 |
Medulla of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla showing medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum and capsule (3). The medullary cords consist of a meshwork of reticular fibers and reticular cells (blue-stained). The cords (1) are more stuffed with lymphocytes and other blood cells. The sinu... | medullar cords; medullar sinus; hilum | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 20 |
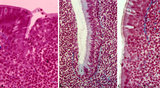 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The combination demonstrates stages of infiltration (=diapedesis) of lymphocytes in the epithelium of the pharyngeal tonsil. The pharyngeal tonsil or adenoid is located in the nasopharyngeal roof. The agglomerations of lymphocytes (4) are covered by (1) pseudostratified ciliated epithel... | pharyngeal tonsil ; GALT; diapedesis; pseudostratified ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 21 |
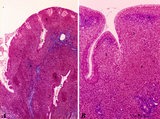 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A: The roof of the nasopharynx is covered by a columnar epithelium with faintly light-stained goblet cells (1) and part of a fold shows cle... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 22 |
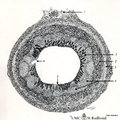 |
Scheme of appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Survey vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tis... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 23 |
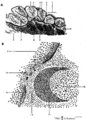 |
Scheme of lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue') | Lingual tonsil (consisting of the accumulation of folliculi linguales). The root of the tongue contains invaginations or crypts or narrow caverns (3). In these crypts the ducts of the mucous glands (8) end up. The crypts are lined by multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium (2) and are sur... | lingual tonsil; scheme; germinal center; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 24 |
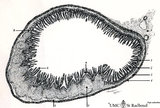 |
Scheme of ileum with Peyers patches (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (dog) | Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria (e.g. respiratory passages, genitourinary tract). The gut-associated lymphatic tissues (GALT) are ... | GALT; follicle; scheme; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 25 |
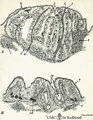 |
Scheme of palatine and pharyngeal tonsils ('lymphoepithelial tissues') (human) | The palatine tonsils are covered by the multilayered, non-keratinizing squamous epithelium of the oral cavity (A-1). In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a multilayered ciliated epithelium (respiratory-like epithelium, B-9). The Waldeyer's tonsillar ring i... | germinal center; scheme; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
