The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
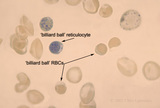 |
'Billiard Ball' Cells | 'billiard ball' cells in Hb SC disease with supravital stain | Fe01aT; Hb SC | Albert Einstein College of Medicine Gallery of Hematology Images |
| 2 |
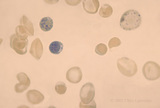 |
'Billiard Ball' Cells | 'billiard ball' cells in Hb SC disease with supravital stain | Fe01a0; Hb SC | Albert Einstein College of Medicine Gallery of Hematology Images |
| 3 |
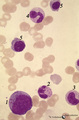 |
(Pro)myelocyte and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte (1) contains coarse primary, azurophilic granules in the basophilic cytoplasm. The absence of nucleoli indicates the late stage of the promyelocyte. (2) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte with toxic granulation (large irregular granules). (3) indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 4 |
 |
1.0 Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones - Introduction | A video introduction to the biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Guide questions -- What types of compounds are included in the class of steroids? Why is it important to know the sources and pathways in the synthesis of steroid hormones? University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Phys... | Biosynthesis; Hormone Deficiency; Steroid Hormones; Excess; Pathways | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 5 |
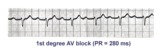 |
1st degree AV block | The normal PR interval is 0.12 - 0.20 sec, or 120 -to- 200 ms. 1st degree AV block is defined by PR intervals greater than 200 ms. This may be caused by drugs, such as digoxin; excessive vagal tone; ischemia; or intrinsic disease in the AV junction or bundle branch system. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 6 |
 |
2.0 Sexual Differentiation and Development - Introduction | Introduction to disorders of sexual differentiation and development. University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Physiology Modules: Part 2.0. Requires the Macromedia Flash Player plug-in. A Blackboard course complete with goals, guide questions and quizzes is the framework for these m... | Steroid Hormones; Hormone Deficiency; Genetic Sex | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 7 |
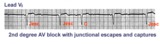 |
2nd degree AV block with junctional escapes and captures | Second degree AV block is present; conducted beats are identified by those QRS's that terminate shorter cycles than the junctional escape cycle; i.e., the 3rd and probably the 4th QRS's are captures; the other QRS's are junctional escapes. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 8 |
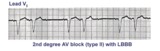 |
2nd degree AV block, mobitz type II, with LBBB | The wide QRS complexes in lead V1 indicates LBBB. 2nd degree AV block, Mobitz II is suggested by the two fixed PR intervals prior to the nonconducted P wave. The location of the block is most likely in the right bundle, because Mobitz II is usually a sign of bilateral bundle branch disease. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 9 |
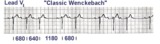 |
2nd degree AV block, type I | The 3 rules of classic AV Wenckebach are: 1. decreasing RR intervals until pause; 2. the pause is less than preceding 2 RR intervals; and 3. the RR interval after the pause is greater than the RR interval just prior to pause. Unfortunately, there are many examples of atypical forms of Wenckebach wh... | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 10 |
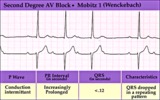 |
2nd degree AV block, type I (Wenckebach) | 2nd degree AV block, type I (Wenckebach) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 11 |
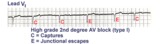 |
2nd degree AV block, type I with escapes and captures | Often in the setting of 2nd degree AV block the pauses caused by nonconducted P waves are long enough to enable escape pacemakers from the junction or ventricles to take over. This example illustrates junctional escapes, labled E and captures, labled C. Note that the PR intervals for the captures ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 12 |
 |
2nd degree AV block, type I, with accelerated junctional escapes and a ladder diagram | The ladder diagram illustrates a Wenckebach type AV block by the increasing PR intervals before the blocked P wave. After the blocked P wave, however, a rev-ed up junctional pacemaker terminates the pause. Note that the junctional beats have a slightly different QRS morphology from the sinus beats... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 13 |
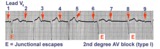 |
2nd degree AV block, type I, with junctional escapes | Junctional escapes are passive, protective events whenever the heart rate slows below that of the escape mechanism. In this example of 2nd degree AV block, type I, the escapes occur following the non-conducted P waves. Arrows indicate the position of the P waves. Note that the escape beats have a... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 14 |
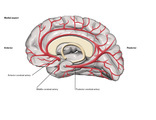 |
3 Major Cerebral Arteries - Midsagittal (Labeled) | Anterior cerebral, middle cerebral, and posterior cerebral arteries. | Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Illustrations | |
| 15 |
 |
3.0 Neuroendocrine Control of Reproduction and Puberty - Introduction | Introduction to the neuroendocrine control of reproduction and puberty. University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Physiology Modules: Part 3.0. Requires the Macromedia Flash Player plug-in. A Blackboard course complete with goals, guide questions and quizzes is the framework for thes... | Steroid Hormones; Reproductive Cyclicity | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 16 |
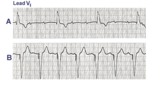 |
3rd degree AV block rx'ed with a ventricular pacemaker | In A the ECG shows complete or 3rd degree AV block with a left ventricular escape rhythm, as evidenced by the upright QRS morphology. In B the artificial right ventricular pacemaker rhythm is shown. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 17 |
 |
4 P' Sign of Amyloid | 4 P' sign of amyloid | Kg010T | Albert Einstein College of Medicine Gallery of Hematology Images |
| 18 |
 |
4 P' Sign of Amyloid | 4 P' sign of amyloid | Kg0100 | Albert Einstein College of Medicine Gallery of Hematology Images |
| 19 |
 |
4.0 Female Reproductive System | Introduction to the coordinated changes in the components of the female reproductive system throughout the menstrual cycle and the causes and effects of menopause. University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Physiology Modules: Part 4.0. Requires the Macromedia Flash Player plug-in. A ... | Steroid Hormones; Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian Axis; Female Reproductive Tract | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 20 |
 |
5.0 Male Reproductive System - Introduction | Introduction to the functions of the male reproductive system. University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Physiology Modules: Part 5.0. Requires the Macromedia Flash Player plug-in. A Blackboard course complete with goals, guide questions and quizzes is the framework for these modules... | Steroid Hormones | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 21 |
 |
The 5q-syndrome in Myelodysplastic Syndrome | the 5q-syndrome in MDS | Mb1200 | Albert Einstein College of Medicine Gallery of Hematology Images |
| 22 |
 |
6.0 Fertilization, Pregnancy and Lactation - Introduction | Introduction to fertilization, pregnancy and lactation. University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Reproductive Physiology Modules: Part 6.0. Requires the Macromedia Flash Player plug-in. A Blackboard course complete with goals, guide questions and quizzes is the framework for these modules. Addit... | Steroid Hormones; Gametes | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 23 |
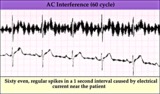 |
60 cycle artifact - marquette | 60 cycle artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 24 |
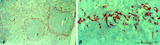 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 25 |
 |
: Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Specialized venules (1) or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are here located in the paracortical area (4) close to the lymphatic follicle (2+3). The HEVs are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific homing receptors for antigen-primed B- and T ly... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
