The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
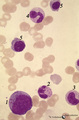 |
(Pro)myelocyte and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte (1) contains coarse primary, azurophilic granules in the basophilic cytoplasm. The absence of nucleoli indicates the late stage of the promyelocyte. (2) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte with toxic granulation (large irregular granules). (3) indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 2 |
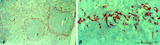 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 3 |
 |
: Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Specialized venules (1) or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are here located in the paracortical area (4) close to the lymphatic follicle (2+3). The HEVs are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific homing receptors for antigen-primed B- and T ly... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 4 |
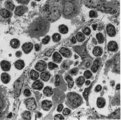 |
: Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. A low magnification of a part of the medulla showing medullary cords surrounded by labyrinthine medullary sinus (*). In this picture the medullar cord runs from left bottom corner to right top corner, and is lined by flat reticular cell types. Within the cord one finds a star-sh... | medulla; electron microscopy; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 5 |
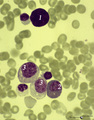 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus and myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Indicates a bare large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte which has totally shed the cytoplasm. These cells are often seen in normal marrow and are ultimately removed by macrophages. There is no cytoplasm left, nor platelets are left around the nucleus. T... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 6 |
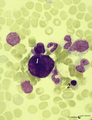 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) indicates a naked, large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte with visible lobes. No cytoplasm nor platelets are left around the nucleus. Most surrounding cells are of myeloid origin, except one orthochromatic erythroblast (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 7 |
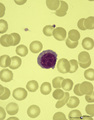 |
A plasmacytoid lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The plasmacytoid lymphocyte is an activated B lymphocyte to be transformed into a plasma cell. The cytoplasm is more basophilic and the chromatin pattern is more clumped than in a virgin small lymphocyte. When the cell contains numerous immunoglobulin inclusions (glo... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 8 |
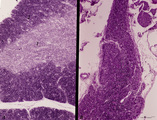 |
Accidental involution of thymus (mouse, malaria infection) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. Due to the infection with malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei in mice) a steroid-related involution of the thymus is induced in mice within 14 days. A: normal thymus with cortex (2) and medulla (1). B: There is still a quite large remnant of the original thymus tissue ... | malaria infection; thymus involution; Plasmodium berghei; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 9 |
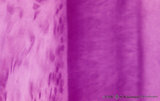 |
Acellular cementum in the tooth (longitudinal segment of coronal half of root; high magnification; human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: periodontal ligament with collagen fibers; flattened cementoblasts followed by a thin seam of pink cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum as collagen fibers protrude from the periodontal ligamen... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; Sharpey's fibers; incremental lines | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 10 |
 |
Acellular cementum in the tooth (longitudinal segment of coronal half of root; human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. From left to right: periodontal ligament with blood vessels; flattened cementoblasts followed by a thin seam of pink cementoid; darker stained acellular cementum, the so-called acellular extrinsic fiber cementum as collagen fibres protrude from the periodontal ligament ... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; Sharpey's fibers; incremental lines | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 11 |
 |
Activated lymphocyte (liver inflammation, human) | Electron microscopy. A cytotoxic T cell (2) is localized within the sinusoid (3) in the liver (8), surrounded by erythrocytes (1) and debris. The lymphocyte with an irregular indented nucleus shows juxta-nuclearly partly swollen Golgi areas (*) and aggregation of mitochondria (4) in the cytoplasm. F... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 12 |
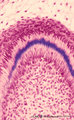 |
Advanced bell stage with ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development - human embryo | Stain: Azan. From top to bottom: Stellate reticulum consisting of a non-vascularized network of ectoderm-derived cells; Cell layers of the stratum intermedium; Columnar (presecretory) ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum intermedium, and at the distal si... | oral cavity; predentin | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 13 |
 |
Afferent lymph vessel in lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left (A) and right (B): part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Left (A): (3) show perpendicularly localized reticular cells and fibres (blue) in the sinus. (4) indicate afferent lymph vessel with valves ... | lymph vessel; subcapsular sinus; follicle; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 14 |
 |
Age involution of thymus (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Although the adipose tissue in the thymus of a patient of 65 years is predominant it still contains areas of remnants (arrows 1+2) of cortical (2) and medullary portions (1) of the thymus. B+C: Degradation of thymic tissues is less progressed in adults and shows less replacement of... | thymus age; thymus involution; adipose cells; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 15 |
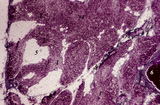 |
Age involution of thymus (human, postpuberal) | Stain: Azan. The size of the thymus is age-dependent, and undergoes a continuous process of involution, starting at postpuberal age. Due to depletion and reduced production of cortical thymocytes, as well as a gradual atrophy of the epithelial cells, the clear distinction between medulla (1) and cor... | thymus age; adipose cells; thymus involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 16 |
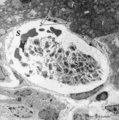 |
Aggregation of platelets (liver, rat) | Electron microscopy. Within a liver sinusoid (S) close to a small bile ductile (B) in the periportal area of the liver some erythocytes (E) and an aggregation of platelets (3) are present. (2) represents the space of Disse to which the liver parenchyma cells border (1). These disc-shaped anucleate p... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 17 |
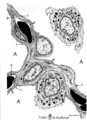 |
Air-blood barrier in the lung (mammals) | Scheme electron microscopy. (1, ↓) Represents type I pneumocytes lining alveolar spaces (A). Cell (2) represents a free alveolar macrophage. The type II pneumocyte (3) is adherent to type I pneumocyte extensions (note junctional connection), and contains multilamellar bodies (surfactant). A myofib... | Pneumocyte type I ; Pneumocyte type II | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 18 |
 |
Alveolar cell type II (pneumocyte II) in an alveolus (dog) | Electron microscopy. At (X) the alveolar space, the bulging alveolar cell type II shows the characteristic multilamellar bodies (*, cytosomes) that contain precusor material of surfactant. The lamellar bodies are responsible for the vacuolated appearance of these cells, and they give rise to surfact... | Pneumocyte II; Alveolar cell type II | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 19 |
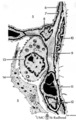 |
Alveolar cells in the lung (mammals) | Scheme electron microscopy. (5) alveolar space; (6) type I Pneumocyte; (7) basal lamina; (8) myofibroblast; (9) collagen and elastin fibers; (10) mesothelial cell of the visceral pleura; (11) capillary with erythrocyte; (12) endothelial cell lining the capillary; (13) type II pneum... | Pneumocyte type I ; Pneumocyte type I I | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 20 |
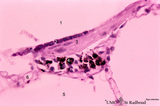 |
Alveolar duct in the lung (mouse) | Stain: PAS and hematoxylin. Part of an alveolar duct lumen (1) that shows bronchiolar characteristics such as cuboidal epithelium (2) covering a bundle of smooth muscle (3) and connective tissue containing macrophages (4) with black pigment deposits. Note PAS-positivity of these cuboidal cells (Clar... | Alveolar ducts; Clara cells | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 21 |
 |
Alveolar macrophage in lung (rat) | Electron microscopy. A wandering alveolar macrophage (1) migrates through an alveolar pore from an alveolar space (A1) into another (A2). Note the dark lysosomal structures and abundant organelles in its cytoplasm. The thin lining type I alveolar cell is hardly discernable (thin arrows →). Interst... | Pneumocyte I; Alveolar macrophages | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 22 |
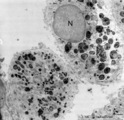 |
Alveolar macrophages in lung (human, adult) | Electron microscopy. Two macrophages in the alveolar space (N = nucleus). Note the heterogeneity of many lysosomal structures containing among others carbon particles and the abundancy of organelles. | Alveolar macrophages | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 23 |
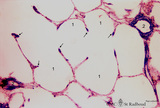 |
Alveolar sac in the lung (human) | Stain: Azan. Characteristic alveolar tips (arrows) of neighbouring thin-walled alveoli (1). The tips contain elastin masked by collagen (blue-stained). At (2) small pulmonary arteries. | Alveolar tips | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 24 |
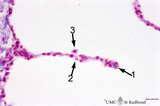 |
Alveolar septum in the lung (human, high magnification) | Stain: Azan. Two neighboring alveoli separated by a septum. (1) points to the tip containing bluish-pink elastin and collagen. The nucleus of a squamous alveolar cell (type I pneumocyte) is indicated by (2), and a free alveolar macrophage by (3). | Alveolar tip; Pneumocyte I | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
| 25 |
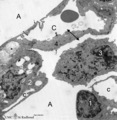 |
Alveolus in lung (dog) | Electron microscopy. (A) indicate alveolar space; (C) indicate capillary with erythrocyte. Drawing-pin represents endothelium. (1) type I alveolar cell; (↓) indicate thin cytoplasm of pneumocyte I. (2) type II alveolar cell. (3) alveolar macrophage. (*) are spots of elastin, intermingled with coll... | Pneumocyte I; Pneumocyte II; Alveolar cells; Alveolar macrophage | Poja Histology Collection - Respiratory System Subset |
