The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
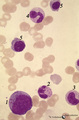 |
(Pro)myelocyte and neutrophilic granulocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The promyelocyte (1) contains coarse primary, azurophilic granules in the basophilic cytoplasm. The absence of nucleoli indicates the late stage of the promyelocyte. (2) segmented neutrophilic granulocyte with toxic granulation (large irregular granules). (3) indicat... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 2 |
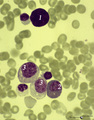 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus and myelocytes in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) Indicates a bare large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte which has totally shed the cytoplasm. These cells are often seen in normal marrow and are ultimately removed by macrophages. There is no cytoplasm left, nor platelets are left around the nucleus. T... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 3 |
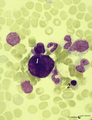 |
A bare megakaryocyte nucleus in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) indicates a naked, large-sized polyploid nucleus of a megakaryocyte with visible lobes. No cytoplasm nor platelets are left around the nucleus. Most surrounding cells are of myeloid origin, except one orthochromatic erythroblast (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 4 |
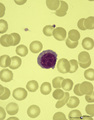 |
A plasmacytoid lymphocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The plasmacytoid lymphocyte is an activated B lymphocyte to be transformed into a plasma cell. The cytoplasm is more basophilic and the chromatin pattern is more clumped than in a virgin small lymphocyte. When the cell contains numerous immunoglobulin inclusions (glo... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 5 |
 |
Activated lymphocyte (liver inflammation, human) | Electron microscopy. A cytotoxic T cell (2) is localized within the sinusoid (3) in the liver (8), surrounded by erythrocytes (1) and debris. The lymphocyte with an irregular indented nucleus shows juxta-nuclearly partly swollen Golgi areas (*) and aggregation of mitochondria (4) in the cytoplasm. F... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 6 |
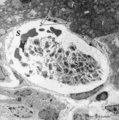 |
Aggregation of platelets (liver, rat) | Electron microscopy. Within a liver sinusoid (S) close to a small bile ductile (B) in the periportal area of the liver some erythocytes (E) and an aggregation of platelets (3) are present. (2) represents the space of Disse to which the liver parenchyma cells border (1). These disc-shaped anucleate p... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 7 |
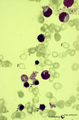 |
Anemic bone marrow smear in iron deficiency (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Due to iron deficiency the erythrocytes (1) look empty, while also the erythroblasts (2) are relatively small and show a ruffled cell border. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 8 |
 |
Anisocytosis of erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows normal human erythrocytes in a blood film, while (B) shows anisocytosis. The small cells are called microcytes. Anisocytosis is an increase in the variability of erythrocyte size beyond that which is observed in a normal healthy subject. It is a common, non... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 9 |
 |
Band and hyper segmented neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (A) shows a young band neutrophil with a non-segmented nucleus. (B) shows mature neutrophils with more than 6 nuclear lobes (hyper segmented). The smear also shows anisocytosis with both microcytes and macrocytes. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 10 |
 |
Band form of neutrophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. From CFU-S (colony forming units-spleen) stem cells arise CFU-GM (colony forming unit-granulocyte/monocyte) stem cells. The latter divide by mitoses and differentiate via promyeloblasts and myeloblasts into neutrophilic myelocytes (the last proliferative stage). The next ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 11 |
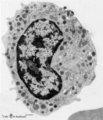 |
Band-form of neutrophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. Transition from late metamyelocyte to band form (9-12 μm). These are the earliest stages of the motile two-lobed neutrophilic granulocytes. (1) a slightly bended nucleus with a nucleolus. (2) Golgi area. Apart from a few mitochondria (3) and profiles of rough endoplasmic retic... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 12 |
 |
Basophilic erythroblast and myeloid cells in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). (1) early basophilic erythroblast. (2) eosinophilic metamyelocyte. (3) neutrophilic myelocyte. (4) two band neutrophils. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 13 |
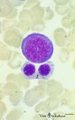 |
Basophilic erythroblast and polychromatic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic erythroblast (1) shows slightly condensed chromatin and a strong basophilic (blue) cytoplasm. In the two polychromatic erythroblasts the chromatin condensation has progressed considerably, and the cytoplasm is much less basophilic. The cells are also s... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 14 |
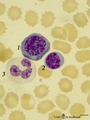 |
Basophilic erythroblast, plasmacytoid lymphocyte and neutrophilic granulocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic erythroblast (1) contains a large, partly condensed but transparent nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm is strong basophilic. The plasmacytoid lymphocyte (2) or activated B cell is much smaller and less basophilic. The young neutrophil (3)... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 15 |
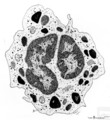 |
Basophilic granulocyte | Scheme electron microscopy. Basophils are non-phagocytic granulocytes that account for 0.5% to 1.0% of the circulating white blood cells. Their granulated cytoplasm stains with basic dyes, hence the name basophil. Electron microscopy reveals a multilobed nucleus (1); few mitochondria (2); numerous ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 16 |
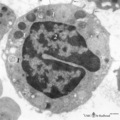 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The bilobed nucleus (2) is surrounded by moderate amount of organelles. The cell exhibits few short filopodia (arrows). The large coarse basophilic granules (1) (specific granules) vary in density and contain vasoactive mediators such as heparin, histamine, sulphated proteoglyca... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 17 |
 |
Basophilic granulocyte (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. The detail shows close to the nucleus characteristic developing basophilic granules (specific granules) (8-13 μm). At thin arrow (↓) a small Golgi area with a small specific granule. At (***) granules with different osmiophilic internal structures. The basophilic granules var... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 18 |
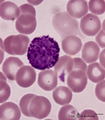 |
Basophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic granulocyte has large, coarse dark purple-stained granules that contain mediators such as eosinophilic chemotactic factors, heparin, histamine, myeloperoxidase. The nuclear lobes are irregular, badly visible and covered by the granules. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 19 |
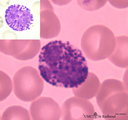 |
Basophilic granulocyte in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic granulocyte is characterized by large, coarse, aggregated dark purple granules. The nuclear lobes are usually not very well visible and masked by the granules (see also inset). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 20 |
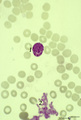 |
Basophilic myelocyte in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The basophilic myelocyte (1) contains dark bluish-purple (metachromatic), coarse granules in the cytoplasm. (2) Platelets. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 21 |
 |
Binucleated plasma cell in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). A large plasma cell with two nuclei. The chromatin is coarsely clumped. The cytoplasm is intensive basophilic due to the large RER content for purpose of antibody production. Note the clear zone (Golgi area) between the nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 22 |
 |
Contamination with osteoblasts of a bone marrow puncture (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In bone marrow smears from a sternum puncture sometimes osteoblasts are found. Osteoblasts may occur in groups, are oval with a usually eccentric, relatively small nucleus. The chromatin is often coarse with 1-3 nucleoli. The cytoplasm is mostly light blue and may co... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 23 |
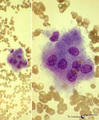 |
Contamination with osteoclasts of a bone marrow puncture (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In the procedure for preparing a bone marrow smear from a sternum puncture osteoclasts are frequently found in the bone marrow smears. The osteoclasts are multinucleated giant cells for the destruction of bone in the process of remodelling and growth. The cytoplasm m... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 24 |
 |
Contamination with squamous cell cells in peripheral blood smear (A) and in a bone marrow smear (B) (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). In blood and bone marrow smears incidentally squamous epithelial cells from the skin tissues are found. (A-1) is an epithelial cell from the keratinized stratified (upper) epidermis; (A-2) a young neutrophil with a few vacuoles in the cytoplasm (probably degeneration... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 25 |
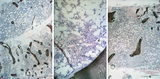 |
Crista biopsies of normal, hypoplastic and malignant bone marrow (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. The composition of three slides shows a normal bone marrow section (A), an aplastic bone marrow (B), and a malignant lymphoma in bone marrow (C). (1) Cristae. (2) Fat tissue or fat cells. (3) Erythrocytes and (4) erythroblasts with dark nuclei. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
