The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
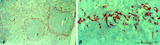 |
: Localization of ED3-positive subpopulation of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining using the antibody ED3. The survey in (A) shows that the ED3-positive macrophages are found as a ring in the marginal zone border, as well as spread in the red pulp area (2). The cells are sometimes referred as marginal metallophilic macrophages. T... | metallophilic macrophages; ED3 antibody; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 2 |
 |
: Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Specialized venules (1) or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are here located in the paracortical area (4) close to the lymphatic follicle (2+3). The HEVs are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific homing receptors for antigen-primed B- and T ly... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 3 |
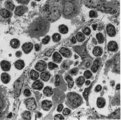 |
: Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. A low magnification of a part of the medulla showing medullary cords surrounded by labyrinthine medullary sinus (*). In this picture the medullar cord runs from left bottom corner to right top corner, and is lined by flat reticular cell types. Within the cord one finds a star-sh... | medulla; electron microscopy; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 4 |
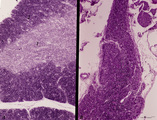 |
Accidental involution of thymus (mouse, malaria infection) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. Due to the infection with malarial parasites (Plasmodium berghei in mice) a steroid-related involution of the thymus is induced in mice within 14 days. A: normal thymus with cortex (2) and medulla (1). B: There is still a quite large remnant of the original thymus tissue ... | malaria infection; thymus involution; Plasmodium berghei; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 5 |
 |
Afferent lymph vessel in lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left (A) and right (B): part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Left (A): (3) show perpendicularly localized reticular cells and fibres (blue) in the sinus. (4) indicate afferent lymph vessel with valves ... | lymph vessel; subcapsular sinus; follicle; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 6 |
 |
Age involution of thymus (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Although the adipose tissue in the thymus of a patient of 65 years is predominant it still contains areas of remnants (arrows 1+2) of cortical (2) and medullary portions (1) of the thymus. B+C: Degradation of thymic tissues is less progressed in adults and shows less replacement of... | thymus age; thymus involution; adipose cells; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 7 |
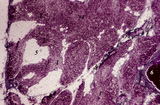 |
Age involution of thymus (human, postpuberal) | Stain: Azan. The size of the thymus is age-dependent, and undergoes a continuous process of involution, starting at postpuberal age. Due to depletion and reduced production of cortical thymocytes, as well as a gradual atrophy of the epithelial cells, the clear distinction between medulla (1) and cor... | thymus age; adipose cells; thymus involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 8 |
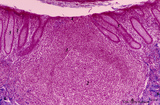 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | A large nodule in the appendix extends through the proper lamina (1) and submucosa. The nodule is similar to that found in a lymph node with germinal centre (2) and darker-stained cap (crescent) (3) orientated towards the lumen of the gut showing a flattened dome area covered with discontinuous epit... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 9 |
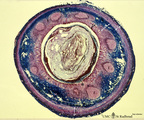 |
Appendix ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey of vermiform appendix (see also Digestive System: Appendix) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the appendix and called gut-associated lymphatic tissue... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 10 |
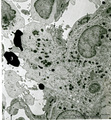 |
Border of a marginal zone in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoelectron microscopy (gold labeling of heparan sulfate in Lowicryl embedding, using the single chain antibody HS4C3). The zone of red pulp immediately surrounding a lymphatic nodule is called the marginal zone (perilymphoid zone) and is composed of a scaffold of basal lamina material w... | marginal zone; immuno electron microscopy; heparan sulfate; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 11 |
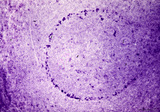 |
Border of white pulp in spleen (mouse) | Monoaminooxidase (enzyme histochemistry on frozen section) with Nitro-BT as staining substrate resulting in a blue formazan precipitate. Despite the general activity of most cells in the spleen, the border cells or so-called metallophilic cells (1) or dendritic antigen-presenting cells (APC) show th... | monoamino oxidase; ED3 antibody; follicle; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 12 |
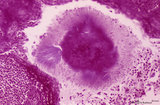 |
Calcified bacterial plaque in palatine tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A tonsillar crypt lined by squamous epithelium (2) that is infiltrated with lymphocytes (1). It is a normal finding that within the crypts free cells, plugs of lymphocytes (1) and calcified epithelial debris as well as colonies of oral commensally bacteria are present. (3) shows a calc... | bacterial plaque | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 13 |
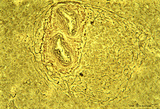 |
Circumscript reticular pattern of splenic lymphatic nodule (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). In this particular case the black-stained reticular network is beautiful organized in and around the nodule. Note also the reticulin staining between the myocytes in the wall of both cross-sectioned (1) central arteries. (2) follicle with lymphocytes. | sinusoid; reticular fibers; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 14 |
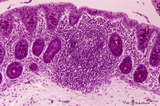 |
Colon ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Hematoxylin-PAS. Solitary lymphatic nodule in colon (see also Digestive System: Colon) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria of the colon and called gut-associated lymphatic tiss... | GALT; follicle; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 15 |
 |
Corpuscles in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A: Several thymic (Hassall's) corpuscles (*) of varying sizes within the medulla (1). The Hassall bodies are surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules. The outer shell consists of more layers of close packed concentrically arranged cells with light-... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 16 |
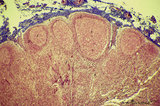 |
Cortex of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. The cortex of the lymph node comprises the (secondary) follicles with germinal centres (1) and corona or mantle zone (2), all filled with B lymphocytes. The paracortical area (3) below the follicles largely comprises T cells. Afferent lymph vessels enter via the capsule (6) into the m... | cortex; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 17 |
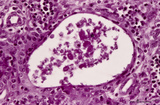 |
Cystic corpuscle in thymus (human, adult) | Stain: Azan. With age the remaining Hassall's corpuscles become more prominent and might represent large multiform structures of over hundreds of microns. The central cells (*) are keratinized. They might be swollen, calcify and become necrotic eventually, or undergo lysis, leaving a large cystic st... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 18 |
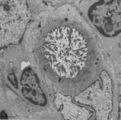 |
Cystic corpuscle in thymus (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. This cystic corpuscle is lined by specialized epithelioreticular cells and exhibits a lumen (1) which is filled with long microvilli however, curiously derived from a flattened epithelial cell (2, nucleus). The cell contains few electron-dense keratohyalin granules (3). (-->) po... | epithelioreticular cells; thymic corpuscle; thymic cyst; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 19 |
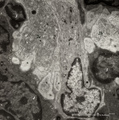 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitations (*) of the left dendritic cells (antigen-presenting cell or APC) (1 and 2a) are clearly shown. The right (2b) is a neighbour dendritic cell sectioned at the level of the Golgi area. (3) lymphocyte and (4) reticular cell. | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 20 |
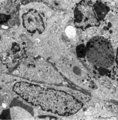 |
Dendritic cells in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The interdigitating dendritic cells (1) (so-called antigen-presenting cell, APC) exhibit numerous slender cell projections (1). (2) shows a macrophage with large lysosomes with heterogeneous contents. Small elongated fibroblastic reticular cells (3) form a structural framework ... | electron microscopy; dendritic cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 21 |
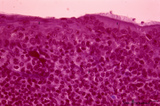 |
Detail of pharyngeal tonsils (human) | Stain: Azan. In contrast to the palatine and lingual tonsils, the epipharyngeal tonsil has a ciliated epithelium (1). Islands of multilayered squamous epithelium may interrupt it (transition zone, 2). The epithelium may be infiltrated with lymphocytes. The surface of this tonsil can be enlarged by m... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; squamous epithelium; ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 22 |
 |
Detailed localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. A: survey white pulp spleen. B: marginal sinuses between PALS area and red pulp. C: red... | white pulp; PALS; heparan sulfate | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 23 |
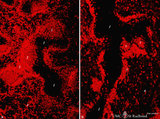 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. A: Normal rat spleen. (1) the dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) filled with T cells. (2) red-stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; immunofluorescence; B lymphocytes | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 24 |
 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on CD3-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section.. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the dark-blue stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thy... | cyclophosphamide; CD3 monoclonal antibody; lymphoid tissue ; immunosuppression | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 25 |
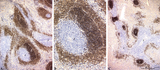 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on splenic B cells (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section of B cells with the antibody Mark-1. The PALS area (1) contains T cells and remains unstained blue. The positively stained B cells (brown) are found in the germinal centres (2) and in the coron... | cyclophosphamide; immunosupression; B lymphocytes; Mark 1 antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
