| Title |
Evaluation of Gas Cofiring Burner Placement Over a Coal Spreader Stoker Boiler |
| Creator |
Drennan, Scott A. |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Date |
1995 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Monterey, California |
| Abstract |
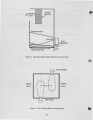
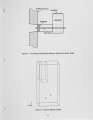
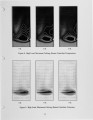
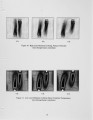
A large amount of industrial and small utility coal fired boilers still exist today in the United States and are under increasing pressure to reduce emissions. In this study, a commercially available CFD code is used to evaluate the proper location of gas cofiring burners over a coal fired spreader stoker boiler. The spreader stoker boiler considered is rated for 165,000 lb/hr steam for electric power generation; however, the boiler is derated to 145,000 lb/hr due to flow limitations. The primary benefits of gas cofiring with coal are (1) reduced carbon loss, (2) reduced NOx, SOx, and CO emissions, (3) recovery of load derate, and (4) improved heat transfer in the furnace. CFD combustion analysis is used to evaluate the design of the burner and its placement in the furnace. It is believed that the majority of the emissions of unburned carbon and CO from a spreader stoker boiler are the result of poor mixing within the furnace, called "channeling." With the introduction of gas cofiring burners, the mixing of the flow above the coal grate is improved providing more uniform temperatures and oxygen concentrations to promote burnout. An arrangement is chosen where two gas cofiring burners are located with one each on opposing side walls of the boiler and an offset distance between the burner centerlines creating a swirling flow pattern in the furnace. The goal of this study is to use CFD to evaluate the offset distance of these gas cofiring burners to maximize mixing above the coal grate without resulting in flame impingement on the boiler walls. The burner placements are evaluated at maximum cofiring rates of 30% of the total boiler load and minimum cofiring of 5% at the minimum boiler load. The gas cofiring burners chosen have maximum capacities of 37 mmBtu/hr and posses 12:1 turn down capability. An optimum burner separation of 8 feet is determined and the burner operational characteristics defined as a result of this study. Modeling data are compared to initial startup performance of the gas cofiring burners. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6jh3prx |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
8570 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6jh3prx |